Fig. 3.
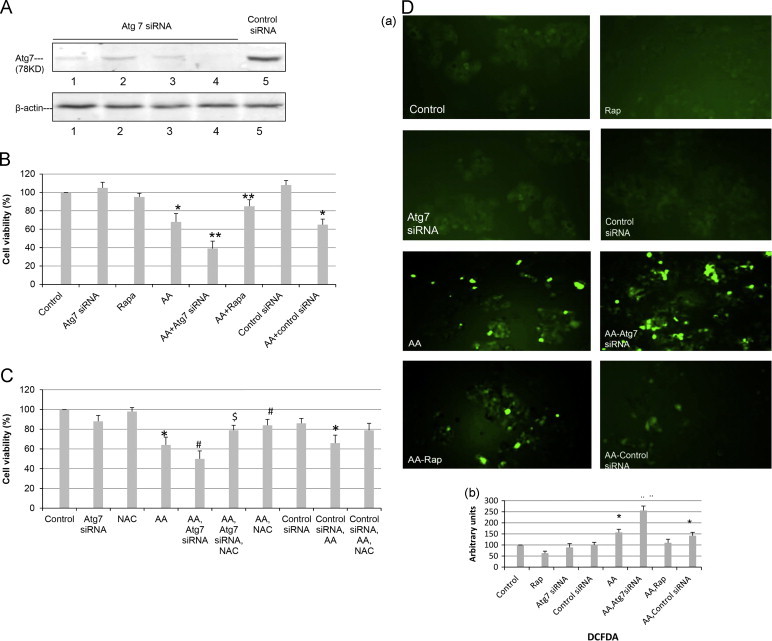
Knockdown of Atg 7 promotes AA induced ROS formation and cytotoxicity. (A) Transfection of E47 cells with Atg 7 siRNA but not control siRNA for 48 h lowers levels of Atg 7. (B) E47 cells were transfected with Atg 7 siRNA or control siRNA for 48 h. Cells were then treated with AA (20 µM) or rapamycin for an additional 48 h and cell viability determined by a MTT assay. (⁎P<0.05 compared with control; ⁎⁎P<0.05 compared with AA alone, N=3.) (C) NAC (5 mM) was added to evaluate the involvement of ROS in AA toxicity and the potentiation of this toxicity by Atg 7 siRNA. (⁎P<0.05 compared with control, #P<0.05 compared with AA alone, $P<0.05 compared with AA plus Atg 7 siRNA, N=3), (D) (a), E47 cells were treated as described in (B); DCFDA (5 µM) was added, and after 15 min incubation, ROS-activated fluorescence was detected under a fluorescence microscope (magnification ×100). (b), Cells were re-suspended in 1×PBS and the intensity of fluorescence determined in a Perkin-Elmer fluorescence spectrophotometer at Ex488/Em530 nm. ⁎P<0.05 compared with control; #P<0.05 compared with AA group, (N=3).
