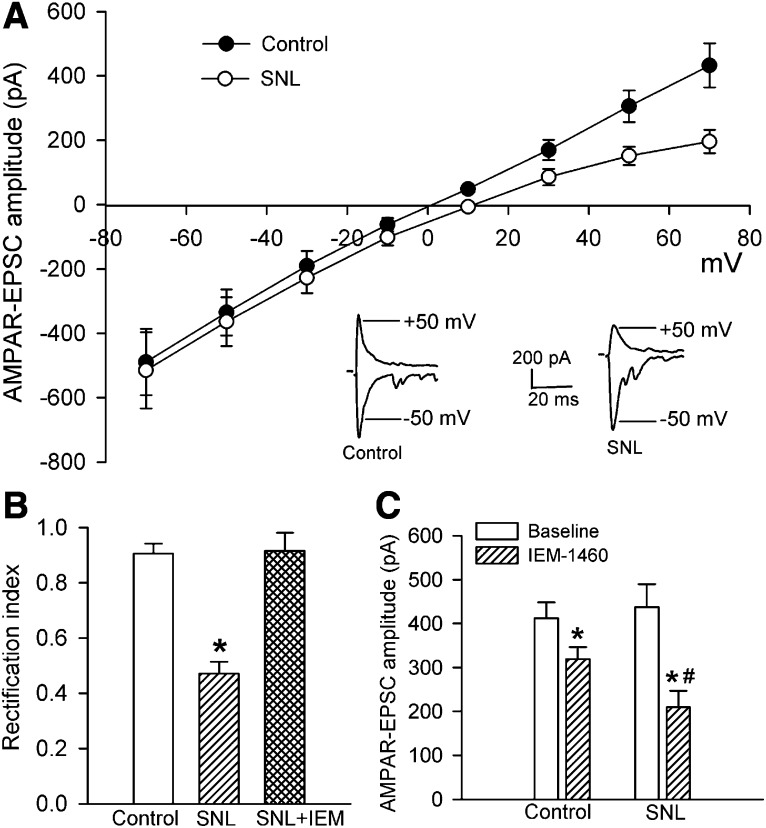
Fig. 1.
Nerve injury induces a switch from predominantly GluA2-containing to GluA2-lacking AMPARs in spinal dorsal horn neurons. (A) Original AMPAR-EPSCs traces (recorded at −50 and +50 mV) and I-V curves of AMPAR-EPSCs of lamina II neurons recorded at holding potentials ranging from −70 to +70 mV in sham control (n = 13 neurons) and SNL rats (n = 10 neurons). (B) Comparison of the rectification index of AMPAR-EPSCs of lamina II neurons in control rats, SNL rats, and SNL rats treated with 100 μM IEM-1460 (n = 8 neurons). (C) Summary data show the effect of 100 μM IEM-1460 on the amplitude of AMPAR-EPSCs of lamina II neurons recorded at a holding potential of −60 mV in control (n = 7 neurons) and SNL rats (n = 8 neurons). *P < 0.05 vs. sham or baseline control group; #P < 0.05 vs. corresponding value in control group.