Fig. 6.
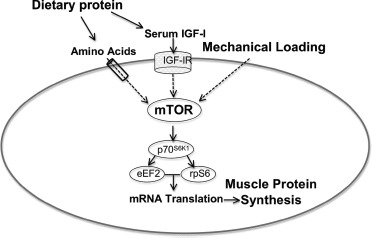
Interaction between dietary protein and mechanical loading on skeletal muscle cell. Dietary protein increases serum amino acids and IGF-I, which, through transporter and receptor localized in the skeletal muscle sarcolemma exert, through a complex intracellular pathway, an anabolic effect. Contractile forces resulting from mechanical loading also stimulate a complex molecular cascade. These pathways impact on the mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTOR), which enhances several translation factors (70-kDa ribosomal protein S6, eukaryotic elongation factor 2, ribosomal protein S6). This simplified illustration schematizes the combined effects of dietary proteins, through amino acids and IGF-I, and mechanotransduction-mediated anabolic cell signaling on skeletal muscle mass and strength. Adapted from Pasiakos [93] (Color figure available online.)
