Fig. 1.
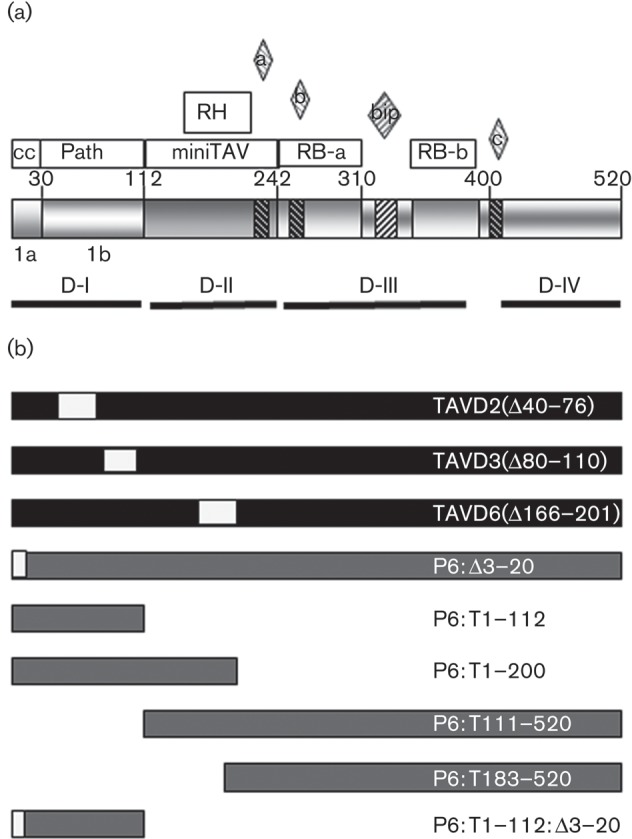
Map of the P6 domains and mutants used in this study. (a) Schematic representation of P6 domains: amino acid numbers at the boundaries of known domains are indicated. Open boxes show the coiled-coil (cc) α-helix, pathogenicity/host-range/avirulence (Path), minimum transactivator (miniTAV), RNase H (RH) and RNA binding (RB-a and RB-b). The bipartite nuclear localization signals (NLS; bip) and three non-conventional NLS (a, b and c) are indicated by diamonds above and cross-hatching. The self-association domains D-I to D-IV and subdomains 1a and 1b are indicated by solid lines. Data from Haas et al. (2005), Haas et al. (2008), Kobayashi & Hohn (2004) and Hapiak et al. (2008). (b) Deletions in P6 coding sequences in CaMV-TAV mutants and in the corresponding P6 expression constructs. Filled boxes indicate sequence from CaMV CM1841, shaded boxes indicate sequence derived from CaMV Cabb B-JI and open boxes indicate internal deletions.
