Figure 3.
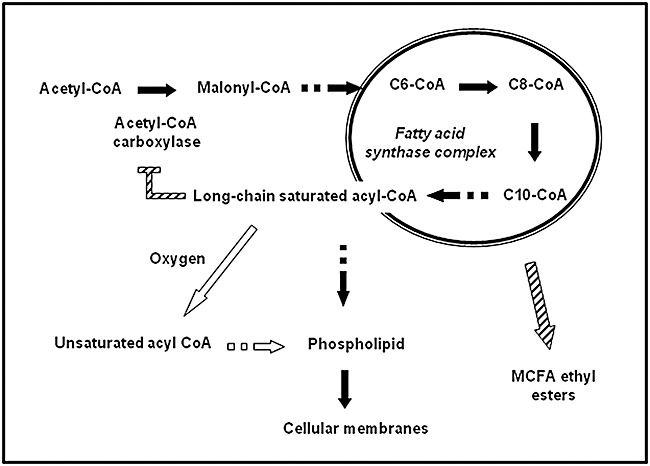
Biosynthesis of fatty acids and its relationship with medium‐chain fatty acid ester formation as proposed by Dufour and colleagues (2003). Acetyl‐CoA carboxylase initiates fatty acid synthesis and is inhibited by long‐chain saturated acyl‐CoAs. As a result, medium‐chain fatty acid CoAs are released from the fatty acid synthase complex, which can then be converted to the corresponding esters. In the presence of oxygen, long‐chain saturated acyl‐CoAs are converted to unsaturated acyl‐CoAs, which do not inhibit acetyl‐CoA carboxylase, and thus no longer cause release of medium‐chain fatty acid CoAs from the fatty acid synthase complex. Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids are used for the synthesis of phospholipids which are then incorporated into cellular membranes.
