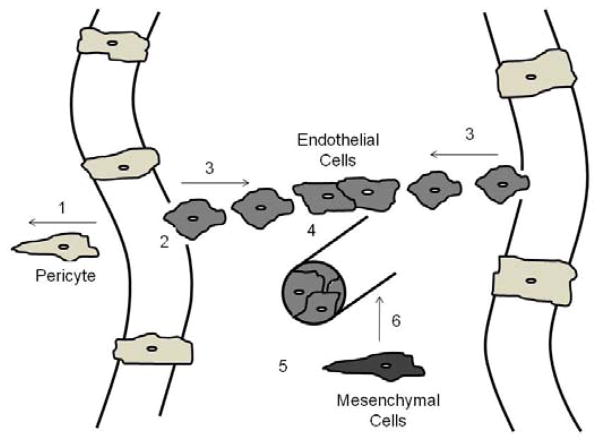
Figure 1.
Steps and factors involved in angiogenesis. Step 1. Vessel destabilization through pericyte removal; angiopoietin (Ang) 2/Tie receptor for Ang1 and Ang2 (Tie2). Step 2. Vessel hyperpermeability and proteolysis of the basement membrane; vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VE cadherin, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). Step 3. Endothelial cell (EC) proliferation and migration; VEGF, fibroblast growth factor (FGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), integrins. Step 4. Cell-to-cell contact; VE cadherin, ephrins. Step 5. Tube formation; FGF, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α 1 (TNF-α). Step 6. Vessel stabilization through mesenchymal cell recruitment and differentiation into pericytes; Ang1/Tie2, PDGF, VE cadherin, TGF-β. Original drawing based on ideas from Papetti and Herman (32).