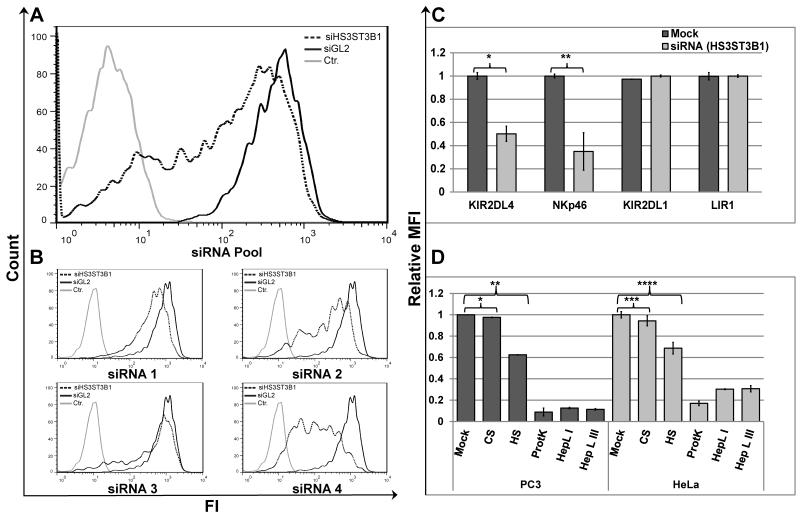
Figure 2. HS3ST3B1-specific siRNA, soluble HS/heparin competition, and HS-specific cleavage prevents binding of KIR2DL4-Ig to PC3 and HeLa cells.
(A) KIR2DL4-Ig staining of PC3 cells transfected with SMARTPool siRNA targeting luciferase (siGL2; bold line) or HS3ST3B1 specific siRNA SMARTPool (dotted line); hFc-Ig staining of control siRNA transfected cells was included as a negative control (grey line). (B) KIR2DL4-Ig staining of PC3 cells transfected with SMARTPool siRNA targeting luciferase (siGL2; bold line) or individual siRNAs from the corresponding SmartPool targeting HS3ST3B1(dotted line); hFc-Ig staining of control siRNA transfected cells was included as a negative control (grey line). Data represent one of n=4 independent experiments for (A) and (B). (C) Comparative staining of KIR2DL4-Ig, NKp46-D2-Ig, KIR2DL1-Ig or LIR1-Ig on PC3 cells transfected with SMARTPool siRNA targeting luciferase (siGL2; Mock) or HS3ST3B1 specific siRNA SMARTPool (siHS3ST3B1). Statistics by T-Test: *p-value 0.005; **p-value 0.01. (D) Comparative staining of PC3 (black bars) or HeLa (grey bars) cells with KIR2DL4-Ig fusion protein under various treatment conditions. Cells were pre-incubated in either DPBS supplemented with 0.5% BSA alone (mock), 5μg/ml of either Heparin LMW (HS) or Chondroitin Sulfate A (CS), or with Proteinase K (ProtK), Heparin Lyase I (HepL I) or Heparin Lyase III (HepL III). KIR2DL4-Ig was used alone (mock and enzyme treated cells) or pre-incubated with either HS or CS for blocking of KIR2DL4-Ig binding. Data represent normalized mean ± s.d. of n=3 independent experiments for (C) and (D). P-values were calculated using T-Test: * p-value and ** p-value ≤ 0.001; *** p-value and **** p-value ≤ 0.01.