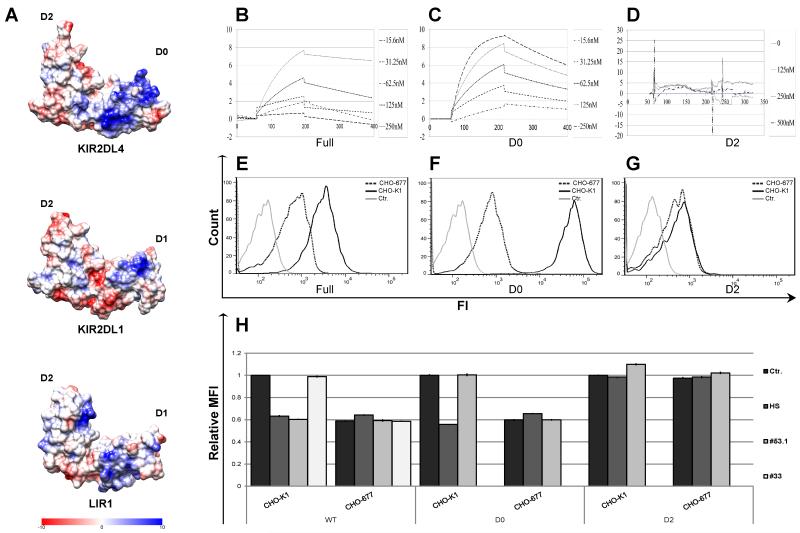
Figure 3. Mapping of the HS/heparin binding site on the KIR2DL4 extracellular domain.
(A) Coulombic charge map of a 3D model of the KIR2DL4 extracellular domain structure. B-D. BIAcore binding-kinetic plots are shown for the interactions of the full structure of KIR2DL4-Ig (B) and individual D0 (C) or D2 (D) Ig-like domains with HS bound on a CM5 sensor chip. Individual lines represent analyses at 2DL4-Ig input concentrations in nM. E-G. Direct binding of KIR2DL4-Ig WT (E), D0 (F) or D2 (G) proteins to parental CHO-K1 cell line (bold line) or the HS-deficient CHO-677 mutant cell line (dotted line) was assayed by FACS. Data represent one of n=4 independent experiments. H. Blocking of FACS-based binding of KIR2DL4-Ig to CHO-K1 or CHO-677 cell lines by HS and anti-KIR2DL4 mAbs. 20μg of KIR2DL4-Ig fusion protein was pre-incubated with either 5μg of HS, CS or 30μg of anti-KIR2DL4 mAb (clones 53.1 or 33) or control mAb (2B4; Ctr.) prior to addition of the mixture to cells. Data represent normalized to Ctr. mean ± s.d. of n=3 independent experiments for (H).