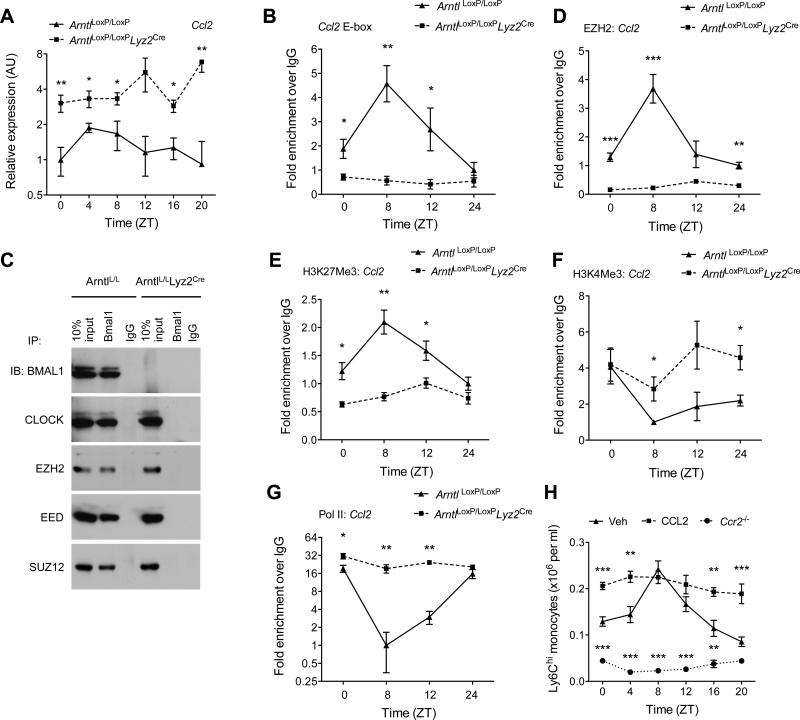
Fig. 4. BMAL1 recruits PRC2 to repress expression of Ccl2.
(A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Ccl2 expression in blood monocytes of ArntlLoxP/LoxP and ArntlLoxP/LoxPLyz2Cre mice kept on a 12 hour day-ligh cycle (n = 3-4 samples per genotype and time point). (B) ChIP analysis of BMAL1 binding to the Ccl2 promoter (n = 4 samples per genotype and time point). (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of BMAL1 and with members of PRC2. Nuclear lysates from serum shocked BMDMs were immunopercipiated with BMAL1 antibody, and immunoblotted for BMAL1, CLOCK, EZH2, EED, and SUZ12. (D and G) ChIP analysis for the recruitment of EZH2 (D) and Pol II (G) to the proximal promoter of the Ccl2 gene (n = 4 samples per genotype and time point). (E and F) ChIP analysis for H3K27Me3 (E) and H3K4Me3 (F) at the proximal promoter of Ccl2 gene (n = 4 samples per genotype and time point). (H) Ly6Chi monocyte numbers in the blood of wild type or Ccr2−/− mice during a 12 hour light-dark cycle. Wild type mice were intraperitoneally injected with PBS (Veh) or CCL2 (20 μgkg−1) 24 hours prior to quantification of Ly6Chi monocytes (n = 4-5 mice per genotype/treatment and time point). Pooled data (A to G) from two independent experiments are shown as mean ± S.E.M and analyzed using two-tailed Student's t-tests (A and B; D to G) and two-way ANOVA (H). *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 represent comparison between ArntlLoxP/LoxP and ArntlLoxP/LoxPLyz2Cre or between wild type treated Veh vs. CCL2 or Ccr2−/− at each time point.