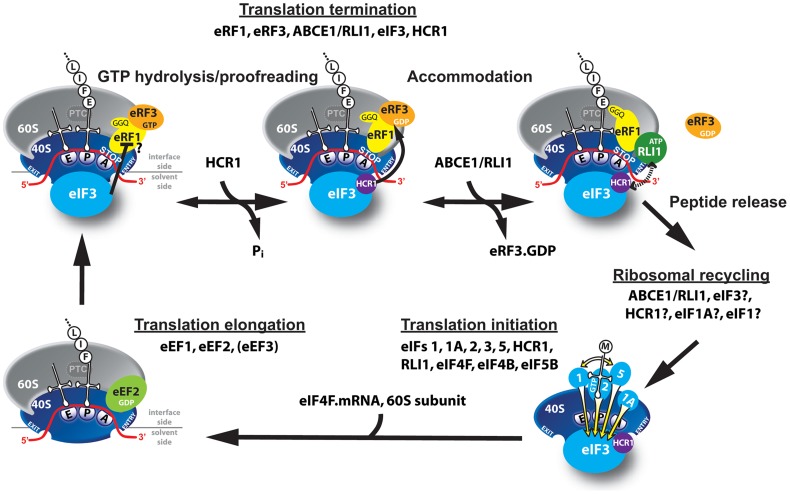
Figure 6. Model of eIF3 and HCR1 involvement in yeast translation termination.
Upon stop codon entry into the ribosomal A-site the pre-TC forms, composed of the canonical release factors eRF1 and eRF3·GTP, and eIF3 and HCR1. eRFs and eIF3 may associate with the pre-TC as a pre-formed unit or alone. In the pre-TC, eIF3 interacts with the N domain of eRF1, via its two small g/TIF35 and i/TI34 subunits, and modulates, perhaps inhibits its stop codon recognition activity during the proofreading step. Upon stop codon recognition the GTP molecule on eRF3 is hydrolyzed. Subsequently, HCR1 promotes eRF3·GDP ejection to allow the ABCE1/RLI1·ATP recruitment to begin the accommodation phase of termination – the eRF1 GGQ motif is pushed to the peptidyl-transferase center (PTC) – during which HCR1 interacts with ABCE1/RLI1. Subsequently, both factors together with eIF3 participate in ribosomal recycling to enable and promote initiation of the next translational cycle (the elongation step is shown only for illustration purposes).