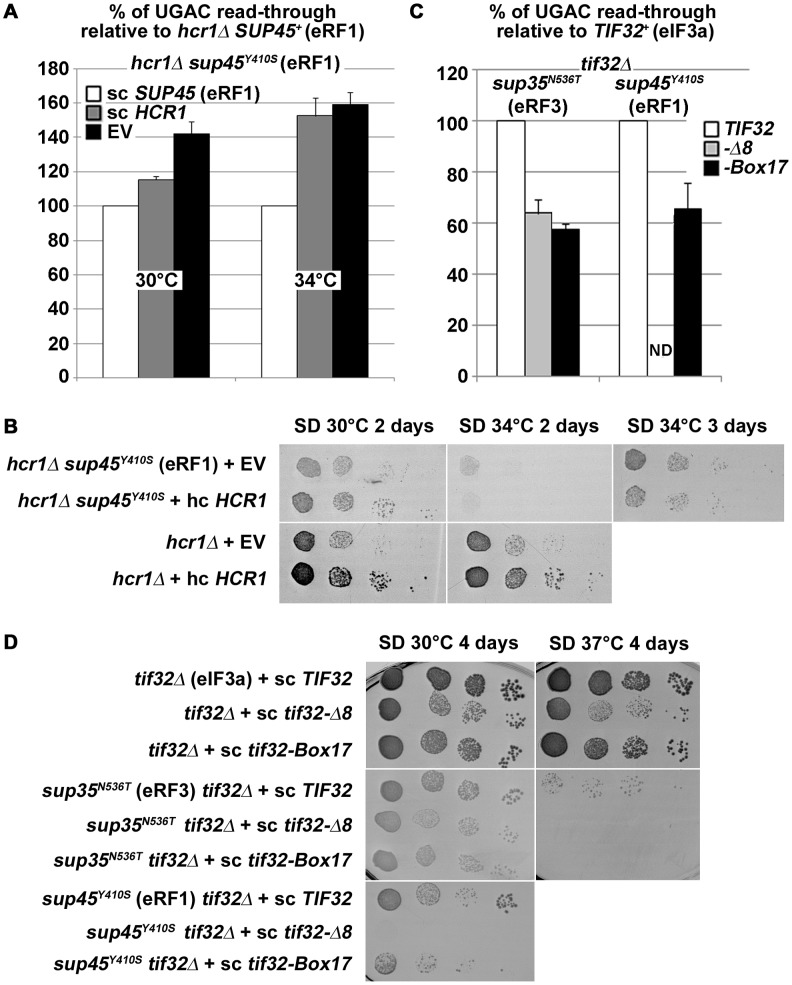
Figure 8. hcr1Δ and eIF3 mutants genetically interact with release factor mutants.
(A–B) The sup45Y410S mutation eliminates the negative impact of hcr1Δ on (A) read-through and (B) growth rates. The hcr1Δ strain was crossed with the sup45Y410S mutant strain and the resulting double mutant was transformed with sc SUP45, hc HCR1, or empty vector (EV), respectively, and (A) processed for stop codon read-through as described in Figure 1 (hcr1Δ read-through values were set to 100%) or (B) subjected to a growth spot assay at indicated temperatures for 2 or 3 days. (C–D) Combining the selected TIF32 mutants with sup35N536T and sup45Y410S (C) reduces their read-through defects and (D) produces synthetic growth phenotypes. The wt and mutant alleles of TIF32 were introduced into tif32Δ, sup35N536T tif32Δ, and sup45Y410S tif32Δ strains, respectively, by plasmid shuffling. (C) The resulting double mutant strains were grown in SD and processed for the stop codon read-through as described in Figure 1 (the read-through values of both single eRF mutants were set to 100%), or (D) spotted in four serial 10-fold dilutions on SD medium and incubated at indicated temperatures for 4 days. ND; not determined due to severe growth deficiency.