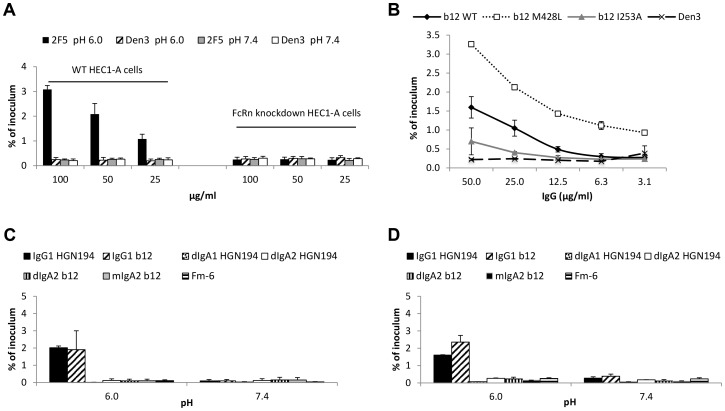
Figure 2. FcRn is responsible for pH/antibody-mediated enhanced transcytosis of HIV-1.
(A) Knockdown of FcRn eliminates enhanced transcytosis. Transcytosis was performed with the wild-type and FcRn knockdown HEC-1A cells in parallel at pH 6.0 or 7.4 using HIV-1US657 (average inoculum = 712,745 RNA copies) and mAb 2F5 or control mAb (Den3). Results represent mean+SE of three independent experiments; p = 0.032 comparing wild type and knockdown cells using 2F5 at pH 6.0 (repeated-measures ANCOVA). (B) An Fc mutant of mAb b12 that increases FcRn binding (M428L) increases transcytosis of HIV-1JRFL at pH 6.0, whereas a mutant that decreases FcRn binding (I253A) reduces transcytosis. Data represent the mean+SE of two independent experiments. (C)(D) IgG1, but not IgA1 or IgA2, enhances transcytosis at pH 6.0. mAb IgG1 b12 or its dimeric (dIgA2 b12) and monomeric (mIgA2 b12) class-switched versions and mAb IgG1 HGN194 or class switched variants dIgA1 HGN194 and dIgA2 HGN194 were tested for transcytosis using (B) HIV-1JRFL Env-pseudotyped virus (average inoculum = 2,269,529 RNA copies) or (C) SHIV1157ipEL-p (average inoculum = 682,724 RNA copies). Fm-6 is an anti-SARS coronavirus IgG1 used as a negative control. All mAbs were tested at 50 µg/ml. Data represent mean+SE of two independent assays for each virus. With either virus, IgG1 versions of the mAbs allow significantly more transcytosis at pH 6.0 than do IgA versions combined (p = 0.025 for HIV-1JRFL pseudoviruses and p = 0.021 for SHIV1157ipEL-p, Kruskal-Wallis test); there is no significant difference between IgG and IgA versions at pH 7.4 (p>0.05).