Figure 1.
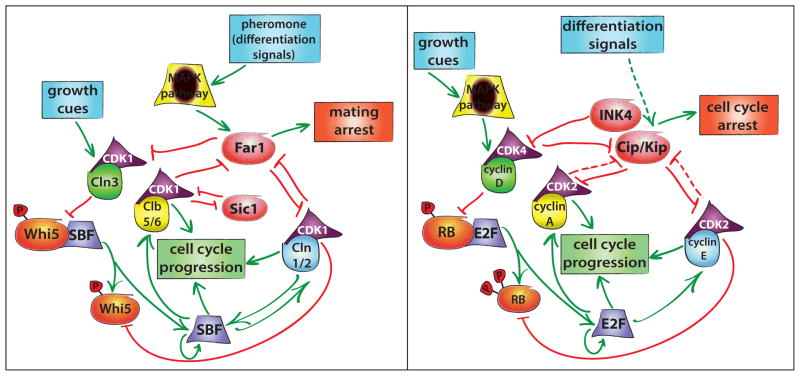
Despite a lack of sequence homology, G1 control networks are similar in both yeast (left panel) and mammals (right panel). Proteins and signals with similar functions are similarly shaped/colored. Upstream growth cues activate G1 cyclins, which drive progression into S phase via the activation of a positive feedback loop. Differentiation signals, including the pheromone-activated MAPK pathway in yeast, activate proteins that inhibit cyclin-CDK activity, leading to the increased stability of a low CDK activity cellular state.