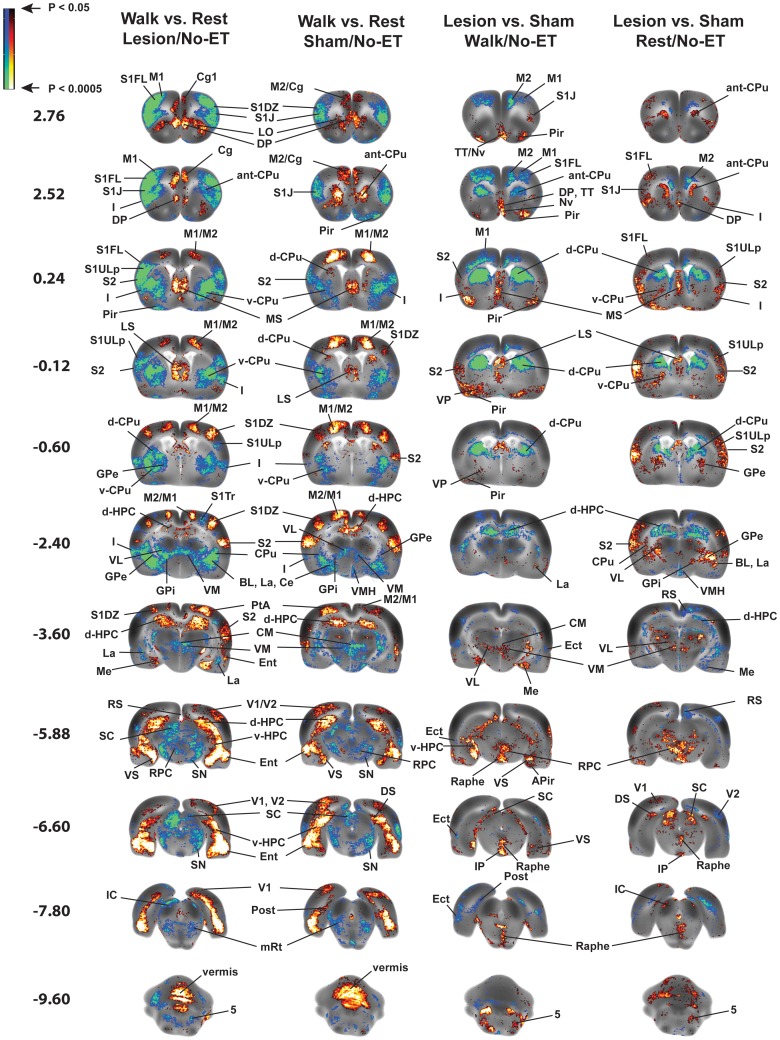
Figure 5. Functional brain activation in rats with bilateral striatal lesions and sham-lesioned rats.
Shown are statistically significant differences in activation during acute treadmill walking (Lesion/Walk/No-ET, n = 9, Sham/Walk/No-ET, n = 10) or at rest (Lesion/Rest/No-ET, n = 10, Sham/Rest/No-ET, n = 9). Comparison highlights lesion effects (Lesion vs. Sham) or the effect of walking (Walk vs. Rest). No exercise training (ET) was given. Depicted is a selection of representative coronal slices (anterior–posterior coordinates relative to bregma). Colored overlays show statistically significant positive (red) and negative (blue) differences. Abbreviations are those from the Paxinos and Watson rat atlas [39]: 5 (trigeminal n., motor, sensory), aca (anterior commissures), BL (basolateral amygdalar n.), Ce (central amygdalar n.), Cg (cingulate cortex), CM (central medial thalamic n.), CPu (striatum: anterior, ant-CPu; dorsal, d-CPu; ventral, v-CPu), d-HPC (dorsal hippocampus), DP (dorsal peduncular cortex), DS (dorsal subiculum), Ect (ectorhinal cortex), Ent (entorhinal cortex), GPe (external globus pallidus), GPi (internal globus pallidus/entopeduncular n.), I (insular cortex), IC (inferior colliculus), IL (infralimbic cortex), IP (interpeduncular n.), La (lateral amygdalar n.), LO (lateral orbital cortex), LP (lateral posterior thalamic n.), LS (lateral septum), M1, M2 (primary, secondary motor cortex), Me (medial amygdalar n.), MS (medial septum), mRT (mesencephalic reticular formation), Nv (navicular n.), PaS (parasubiculum), PH (posterior hypothalamus), Pir (piriform cortex), Pn (pons), PrL (prelimbic cortex), PtA (parietal association cortex), RPC (red n.), RS (retrosplenial cortex), S1DZ, S1FL, S1J, S1Tr, S1ULp, (primary somatosensory cortex: dysgranular, forelimb, jaw, trunk, upper lip), S2 (secondary somatosensory cortex), SC (superior colliculus), SN (substantia nigra), STN (subthalamic n.), TT (tenia tecta), vermis (2nd, 3rd cerebellar simple lobule), V1, V2 (primary, secondary visual cortex), v-HPC (ventral hippocampus), VL (ventral lateral thalamic n.), VM (ventromedial thalamic n.), VMH (ventromedial hypothalamus), VPL/VPM (ventral posterolateral, ventral posteromedial thalamic nuclei), VP (ventral pallidum), VS (ventral subiculum), ZI (zona inserta).