Figure 3. 5,7-DHT lesions do not affect motor activity and anxiety behavior whereas learning and memory processes are impaired.
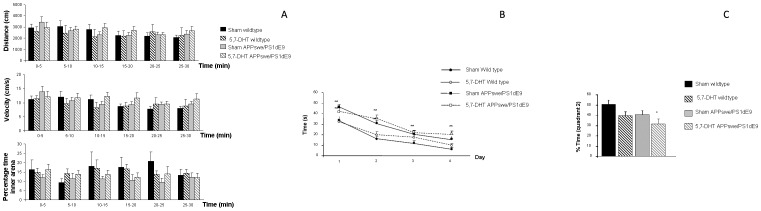
A) No differences were observed among groups by two-way ANOVA (timexgroup) when total distance travelled [F(15,65) = 1.578, p = 0.105] or velocity were measured [F(15,65) = 1.208, p = 0.289]. No differences were observed in the percentage of time that animals spent in the inner area of the open field [F(15,63) = 0.714, p = 0.761]. B) During the acquisition phase in the Morris water maze test we detected a significant treatmentXday effect, and further assessment along individual days, by one-way ANOVA revealed a significant impairment in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice to locate the platform. Day 1: [F(3,172) = 9.213, **p<0.001 vs. sham wildtype and 5,7-DHT wildtype], day 2: [F(3,172) = 16.155, **p<0.001 vs. sham wildtype and 5,7-DHT wildtype], day 3: [F(3,172) = 4.186, **p = 0.007 vs. sham wildtype], day 4: [F(3,172) = 9.329, **p<0.001 vs. sham wildtype and 5,7-DHT wildtype]. C) During the retention phase we detected that wildtype lesioned mice and APPswe/PS1dE9 mice spent shorter times in the quadrant wher the platform used to be located (quadrant 2) however one-way ANOVA for independent samples only reached statistical significance in case of 5,7-DHT APPswe/PS1dE9 treated mice [F(3,37) = 2.947, *p = 0.045 vs. sham wildtype].
