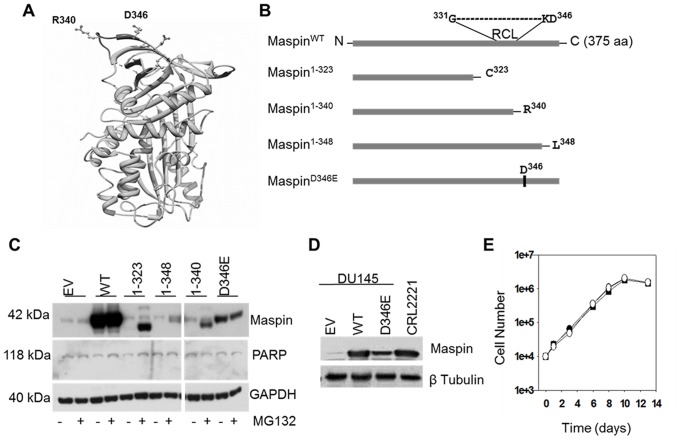
Figure 1. Construction and expression of rational maspin mutants.
(A) Ribbon representation of human maspin generated by UCSF Chimera (http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/). Relative positions of reactive center loop (RCL) p′ site R340 and neighboring D346 residue are depicted as ball and stick model. (B) Schematic illustration of the wild type human maspin and four rational maspin mutants. Relative positions of RCL and D346 in a primary maspin sequence are depicted. The full-length, wild type maspin was denoted as maspinWT, the truncation mutants are maspin1–323 (C-terminal deletion starting 16 amino acids upstream of RCL), maspin1–340 (C-terminal deletion after R340) and maspin1–348 (C-terminal deletion after L348) and the point mutant is maspinD346E. (C) Western blot of maspinWT and four rational mutants re-expressed in prostate cancer cell line DU145 by adenoviral vector (multiplicity of infection, MOI = 30) in the presence or absence of proteasome inhibitor MG132 (5 µM, 6 hrs treatment). Infection of DU145 cells by adenovirus empty vector (EV) was used as a negative control. PARP was used to monitor cell viability after infection and MG132 treatment. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (D) Western blot of recombinant maspin in DU145 cells three days post-infection relative to the expression of endogenous maspin by CRL2221 cells. β tubulin was used as a loading control. (E) Growth curves of infected DU145 cells expressing either maspinWT (•), maspinD346E (○) or empty vector control (▪).