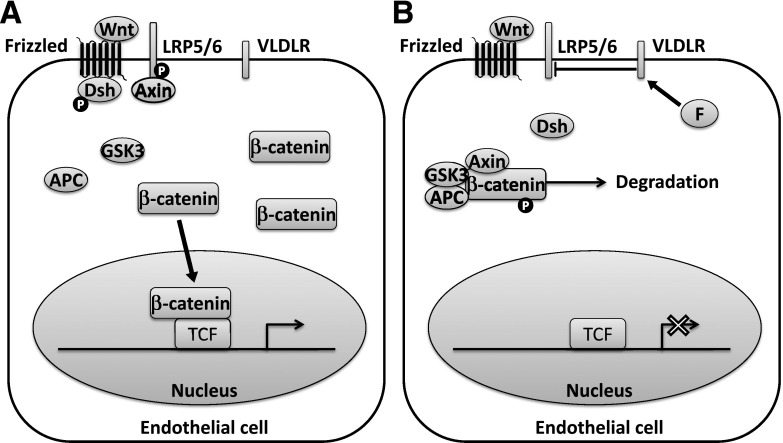
FIG. 4.
Canonical Wnt signaling in an endothelial cell. A: Wnt ligand induces recruitment of dishevelled (Dsh) and Axin to the Frizzled receptor and LDL receptor–related protein (LRP) coreceptor, respectively, and inhibition of the β-catenin destruction complex. This allows β-catenin to accumulate in the cytoplasm and translocate to the nucleus, where it binds with T-cell factor (TCF) and activates transcription of proangiogenic genes. B: Fenofibrate (F) appears to inhibit Wnt signaling through inhibition of LRP6 phosphorylation. The mechanism is not completely understood but may involve upregulation of the VLDL receptor (VLDLR). APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase-3; P, phosphate.