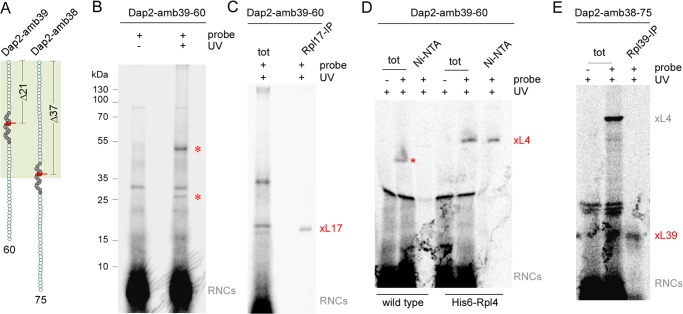
FIGURE 3.
Identification of contacts between a nascent SA and the tunnel proteins Rpl4, Rpl17, and Rpl39. A, schematic representation of 60-residue Dap2-amb39 containing a probe in position PTC-Δ21, and 75-residue Dap2-amb38 containing a probe in position PTC-Δ37. The ribosomal tunnel is indicated in palegreen, the SA of Dap2 is shown in dark gray, and the probe is shown in red. The length of the nascent chains and the distance to the PTC is indicated. B, UV cross-linking pattern of nascent Dap2-amb39-60. Wild type RNCs carrying radiolabeled FLAG-tagged nascent chains, were photolyzed (+ UV), or, as a control, were kept in the dark (−UV). Subsequently, cross-linked products were purified via anti-FLAG beads and were analyzed on Tris-Tricine gels followed by autoradiography. The two major cross-linking products are labeled with a red asterisks. Positions of prestained molecular mass marker proteins are indicated. Note that the N-terminal FLAG tag on the nascent chain, which was employed to enrich the cross-link products, was not included in the calculation of the nascent chain length. C, identification of a cross-link between Rpl17 and Dap2-amb39-60. Wild type RNCs carrying radiolabeled Dap2-amb39-60 were photolyzed as described in B. Subsequently, cross-link products to Rpl17 were immunoprecipitated under denaturing conditions using anti-Rpl17 coupled to protein A-Sepharose beads (Rpl17-IP). xL17 indicates the cross-link product between Dap2-amb39-60 and Rpl17. D, identification of a cross-link between Rpl4 and Dap2-amb39-60. RNCs carrying radiolabeled Dap2-amb39-60 were generated in a wild type (wild type) or His6-Rpl4 (His6-Rpl4) translation extract. As a control, unmodified Lys instead of ϵANB-Lys was incorporated into the nascent chains (−probe). After photolysis, samples were subjected to Ni-NTA affinity purification. xL4 indicates the cross-link product between Dap2-amb39-60 and His6-Rpl4. The red asterisk indicates the cross-link to wild type Rpl4, which runs at a lower molecular mass. E, identification of cross-link between Rpl39 and Dap2-amb38-75. RNCs carrying radiolabeled Dap2-amb38-75 were generated in a wild type translation extract. After photolysis, cross-links to Rpl39 were immunoprecipitated using anti-Rpl39 coupled to protein A-Sepharose beads (Rpl39-IP). xL39 indicates the cross-link product between Dap2-amb39-60 and Rpl39. Analysis of the samples in C–E was as described in B. The total (tot) represents 10% of material employed for immunoprecipitation reactions (C and E) or Ni-NTA purification reactions (D).