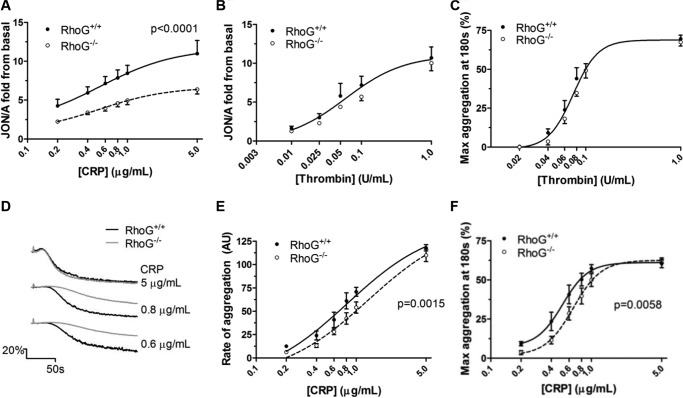
FIGURE 3.
A, inside-out signaling to integrin αIIbβ3 activation in WT and RhoG−/− platelets assessed by flow cytometry. Stimulation of platelets with CRP in the presence of 2 mm CaCl2 led to dose-dependent increases in JON/A binding, indicating increasing integrin activation. Compared with WT platelets, integrin activation was significantly reduced in RhoG−/− platelets (p < 0.0001 by extra sum-of-squares F-test). B, on stimulation with thrombin, however, there was no significant difference between integrin activation in WT and RhoG−/− platelets. C, as with measurements of integrin activation, thrombin-stimulated aggregation was normal in RhoG−/− platelets. D–F, the defect in integrin activation downstream of GPVI noted in the RhoG−/− platelets translated into significant reductions (by extra sum-of-squares F-test) in the rate and maximum extent of CRP-induced aggregation. Data are presented as means ± S.E. from at least five mice/group.