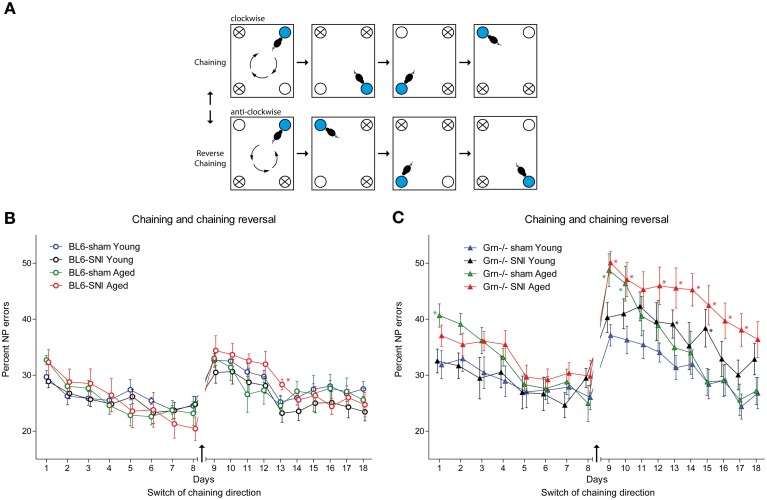
Figure 6.
Spatial sequence learning in young and aged C57BL6/J and progranulin deficient (Grn−/−) mice. (A) Illustration of the “chaining” and “reversal of chaining” tasks. Mice were randomly allocated to either starting with the clockwise or anti-clockwise direction. After 8 days the direction was conversed. The blue circle indicates the awarding corner and the white circle is the corner, in which the next water award was applied. The crossed circles show the corners where water access was denied. (B,C) Time courses of nosepoke error percentages (mean ± s.e.m) per day in C57BL6/J and progranulin deficient (Grn−/−) mice, n = 8 per group during “chaining” and “reversal of chaining.” rm-ANOVA revealed significant differences between SNI-treated aged mice as compared to young mice, P < 0.05. In progranulin deficient mice, SNI also caused an increase in the error rate in young mice. Time points which differed significantly vs. the sham treated young mice are indicated per asterisks, P < 0.05.