Figure 1.
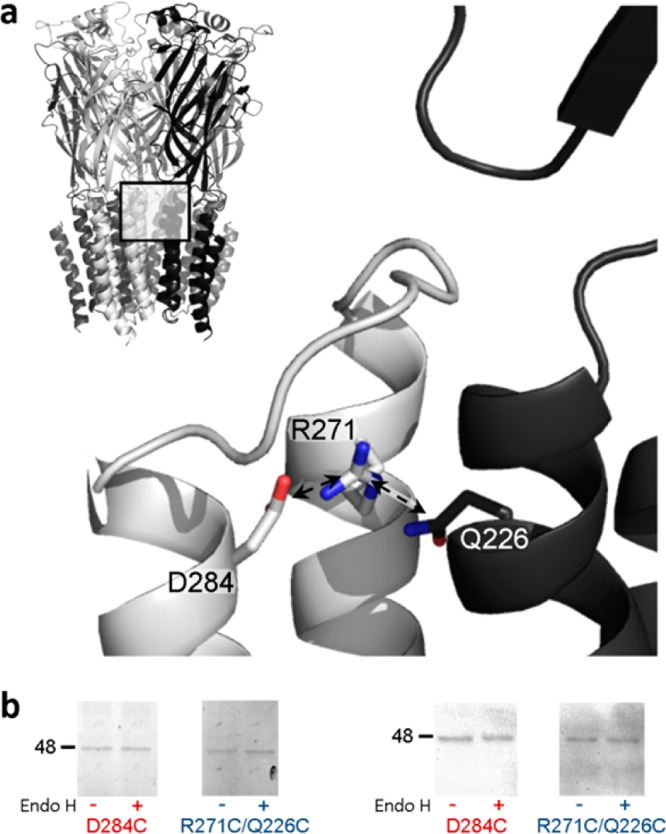
(a) Position of R271 and proximal residues in the α1 GlyR homology model. The pentameric structure is shown (top left), and the interface of two adjacent subunits (boxed area) is shown in greater detail, with one subunit colored gray and one black. Arrows indicate the 4.1 and 3.6 Å separation of M2-R271 ζC from M3-D284 γC and M1-Q226 δC, respectively. The distance from the M2-R271 ζC atom to that from adjacent subunits is 20.5 Å (not shown). The model, which was described previously,18 used as a template the glutamate- and ivermectin-activated C. elegans α GluCl crystal structure16 (Protein Data Bank entry 3RIF). (b) Cell surface expression of mutant α1 GlyR subunits. Oocytes were treated with mutant D284C or R271C/Q226C α1 GlyR cRNAs and either rinsed with the membrane-impermeable fluorophore Cy5, purified, separated by SDS–PAGE, and imaged (left) or separated by SDS–PAGE, subjected to α1 GlyR-specific Western blotting, and imaged. Both experiments identified single α1 GlyR subunits (∼48 kDa protein bands) that were insensitive to Endo H cleavage, indicating cell surface expression. Electrophysiological experiments showed that D284C α1 GlyRs were not responsive to glycine, whereas R271C/Q226C α1 GlyRs were.
