FIGURE 3.
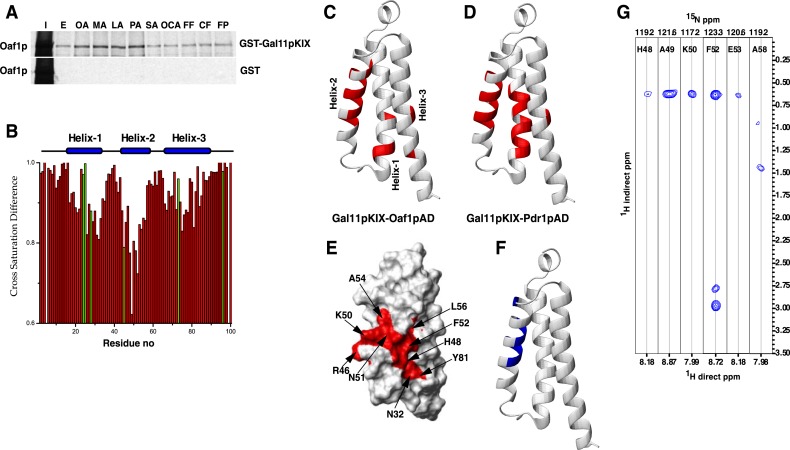
The Gal11p/MED15 KIX domain interacts with Oaf1p in a fatty acid-stimulated manner. A, activating fatty acids (OA, MA, LA, and PA) enhance interaction between Oaf1p and the Gal11p/MED15 KIX domain, whereas non-activating fatty acids SA and oleoyl-CoA (OCA), as well as peroxisome proliferators/NSAIDs, do not significantly affect this interaction. The 35S-labeled in vitro synthesized Oaf1p was subjected to GST pulldown experiments using glutathione-Sepharose beads bound to GST or GST-Gal11p/MED15 KIX proteins in the presence of fatty acids or peroxisome proliferators/NSAIDs as mentioned above. I represents 10% input, and E (for EtOH) represents vehicle control. B, cross saturation transfer difference (ratio of saturated to non-saturated) of a complex of Gal11p/MED15 KIX with Oaf1pAD-9 in the molar ratio 1:1. The resonances of the residues represented in green exhibit significant overlap. Residue no, residue number. C, ribbon representation of the Gal11p/MED15 KIX domain, with the residues that are significantly affected (>15% reduction in intensity) in cross saturation transfer experiments with Oaf1pAD-9 peptide highlighted in red. D, ribbon representation of Gal11p/MED15 KIX highlighting the residues affected in cross saturation transfer experiments with Pdr1pAD-12. E, surface representation of Gal11p/MED15 KIX highlighting some of the residues significantly affected by cross saturation transfer with Oaf1pAD-9. F, ribbon representation of Gal11p/MED15 KIX with residues that have intermolecular NOE cross peaks with Oaf1pAD-9 highlighted in blue. G, strips from the 15N-dispersed NOESY spectrum showing intermolecular to the amide protons in helix 2 of Gal11p/MED15 KIX.