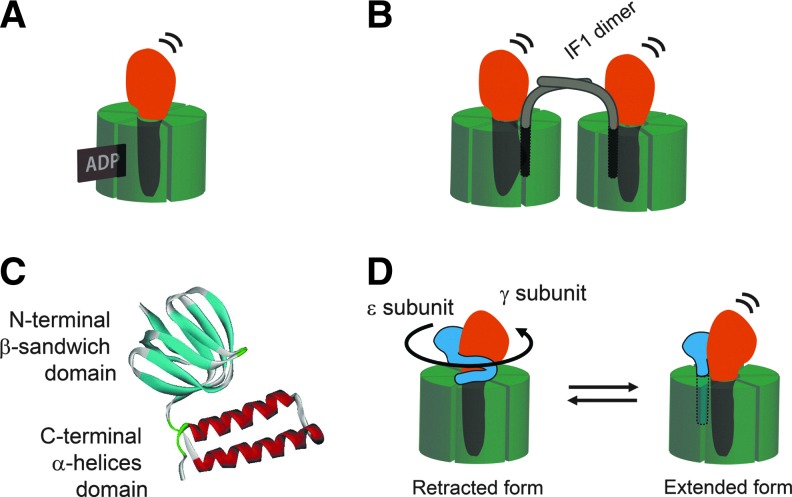
FIG. 2.
Regulatory mechanism for ATP synthase. (A) Tightly bound ADP inhibits ATP hydrolysis activity. (B) IF1 is the intrinsic ATPase inhibitor for MF1. (C) The ɛ subunit is composed of two domains: the N-terminal β-sandwich domain and C-terminal α-helices domain. The latter domain is structurally variable. The NMR structure of the ɛ subunit from Thermosynechococcus elongatus BP-1 (PDB:2RQ6) is shown. For more detail, see Ref. (67). (D) The extended conformation of the ɛ subunit inhibits the ATPase. IF1, intrinsic ATPase inhibitor protein; MF1, F1 part of mitochondrial ATP synthase.