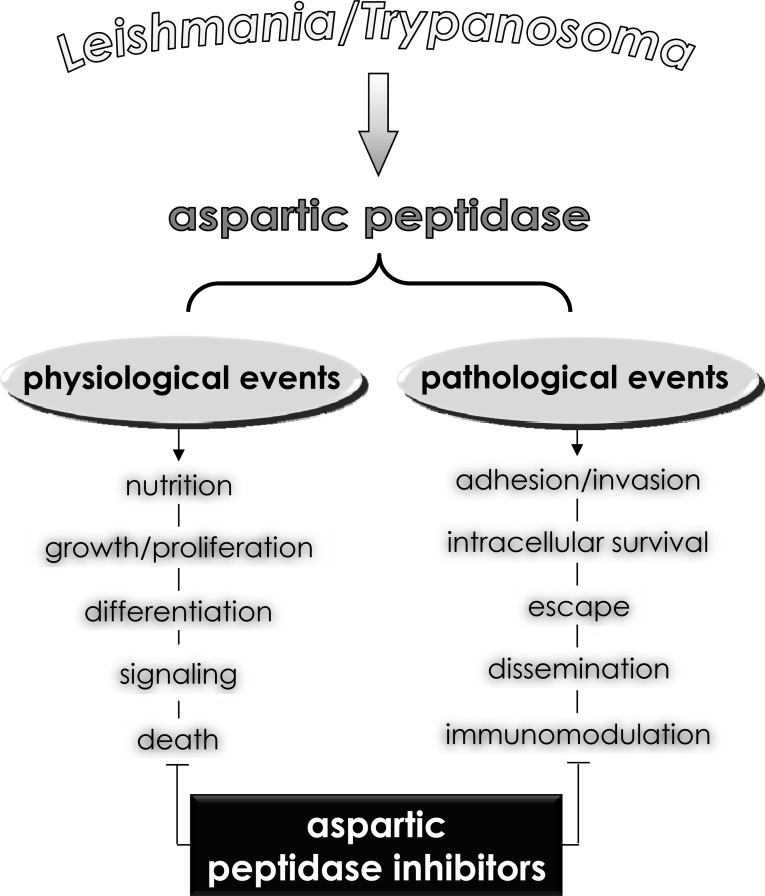
Fig. (10).
Possible roles played by aspartic-type peptidases produced by human pathogenic trypanosomatids belonging to the Leishmania and Trypanosoma genera. Aspartic peptidases contribute to maintaining basic metabolic processes in trypanosomatid cells, which govern crucial biological events including proliferation, differentiation as well as signaling and death pathways. In addition, aspartic peptidases can also participate in different contexts of the trypanosomatid-host interface, facilitating some pathogenic events such as dissemination, adhesion, escape, nutrition and immunomodulation of the host immune responses. Consequently, aspartic peptidase inhibitors are able to block one or several of these fundamental events, reducing the ability of these trypanosomatids in causing infections.