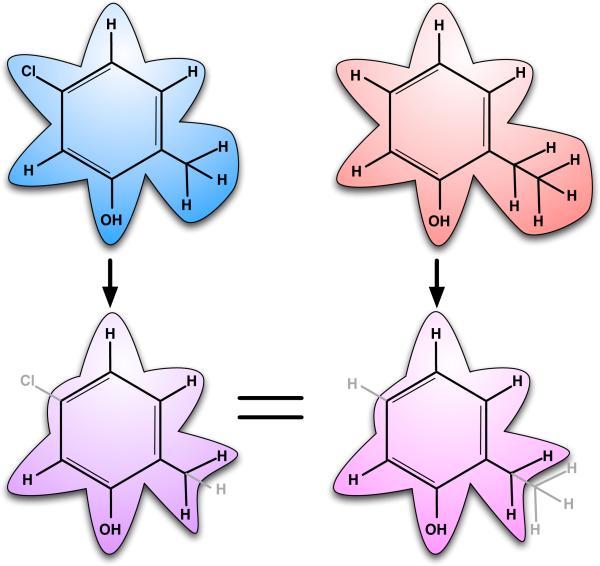
Fig. 4.
Single topology, explicit intermediate free energy calculations. Here, these calculations would be used to compare binding of 5-chloro-2-methylphenol and 2-ethylphenol. Fully interacting atoms are shown in black with underlying shaded contours, while noninteracting atoms (dummy atoms) are shown in gray with no shaded contours. The intermediate (scaffold) is specified explicitly, at the bottom. At left, the chlorine atom and one hydrogen are changed into dummy atoms, while at right, one hydrogen atom and a methyl group are changed into dummy atoms. The two scaffolds at bottom differ in number of dummy atoms, though these contributions cancel when computing free energies. The free energy calculation involves turning the specified atoms into dummy atoms in both molecules.