Fig 2.
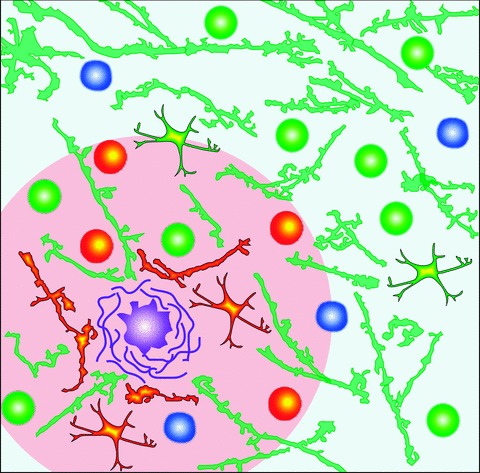
Pathological changes in brain parenchyma in the vicinity of amyloid plaques. Schematic drawing illustrating an amyloid plaque (purple) surrounded by neurons (circles), dendrites (branches) and astrocytes (branched cells). Three different types of neurons are illustrated: normally active neurons (white-green), hyperactive neurons (yellow-red) and silent neurons (white-blue; [90]). Dendritic branches with an increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration are coloured yellow-red while the ones with normal resting [Ca2+]i appear green [88]. The pacemaker astrocytes initiating propagating [Ca2+]i waves are shown in yellow-red and the rest of the astrocytes (having an increased resting [Ca2+]i) are shown in yellow-green [91]. Note that most of the changes in the intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis are restricted to the immediate plaque vicinity (an area situated less than 60 μm from the plaque border, coloured in pink).
