Fig 2.
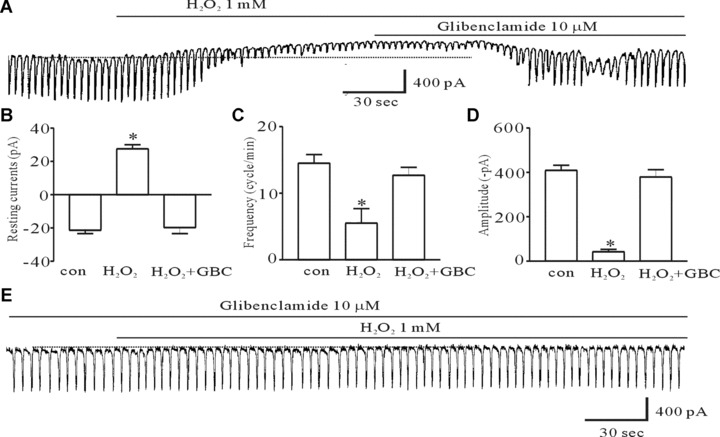
The effect of glibenclamide, an inhibitor of ATP-sensitive K+ channels, on H2O2-induced action on pacemaker currents of ICC from the murine intestine. (A) Pacemaker currents exposed to 1 mM H2O2 at a holding potential of −70 mV. The H2O2-induced effects were reversed by adding 10 μM glibenclamide. (B, C, and D) The inhibitory response to glibenclamide on the H2O2-induced action on pacemaker currents. (E) The effect of 1-mM H2O2 on pacemaker currents after pretreating cells with 10 μM glibenclamide. The bars represent mean ± S.E. values (n= 6). Asterisks indicate significantly different from the controls (P < 0.05), and the dotted lines indicate zero current levels. glibenclamide, GBC.
