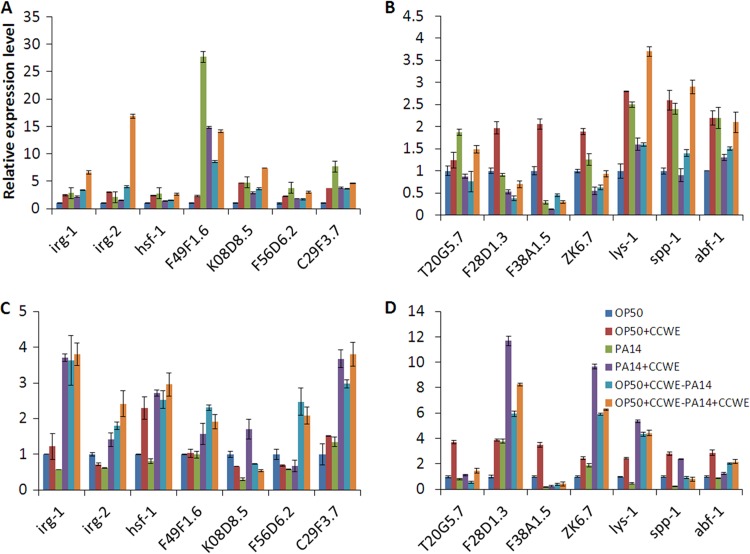
Fig 3.
CCWE-induced immune responses in wild-type C. elegans. N2 worms were grown with or without dietary supplementation with CCWE, and expression of immune genes was analyzed by qPCR at 6 h (A and B) or 24 h (C and D) of adulthood or postexposure to P. aeruginosa PA14 that was preestablished with or without CCWE. Worms fed Escherichia coli strain OP50, the standard laboratory food source, were used as a control for noninfection conditions, and OP50-fed PA14-infected worms were used as a control for infection conditions. OP50, worms fed OP50; OP50 + CCWE, worms fed OP50 with CCWE as food supplement; PA14, worms grown with OP50 and exposed to PA14; PA14 + CCWE, worms grown with OP50 and exposed to PA14 which was cultured in the presence of CCWE; OP50 + CCWE-PA14, worms raised on OP50 with CCWE as a food supplement and exposed to PA14; OP50 + CCWE-PA14 + CCWE, worms raised on OP50 with CCWE as food supplement exposed to PA14 which was cultured in the presence of CCWE. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. P was <0.0001 for OP50 versus OP50 + CCWE for all genes except T20G5.7 (A and B); P was <0.0001 for OP50 versus OP50 + CCWE for all late immune response genes (D); P was < 0.05 for OP50 versus OP50 + CCWE for hsf-1 and C29F3.7 (C); P was <0.0001 for PA14 versus PA14 + CCWE, OP50 + CCWE-PA14, or OP50 + CCWE-PA14 + CCWE for irg-1, irg-2, and K08D8.5 (A) and for F38A1.5, lys-1, and spp-1 (B); P was <0.01 for PA14 versus PA14 + CCWE, OP50 + CCWE-PA14, or OP50 + CCWE-PA14 + CCWE for all genes (C and D).