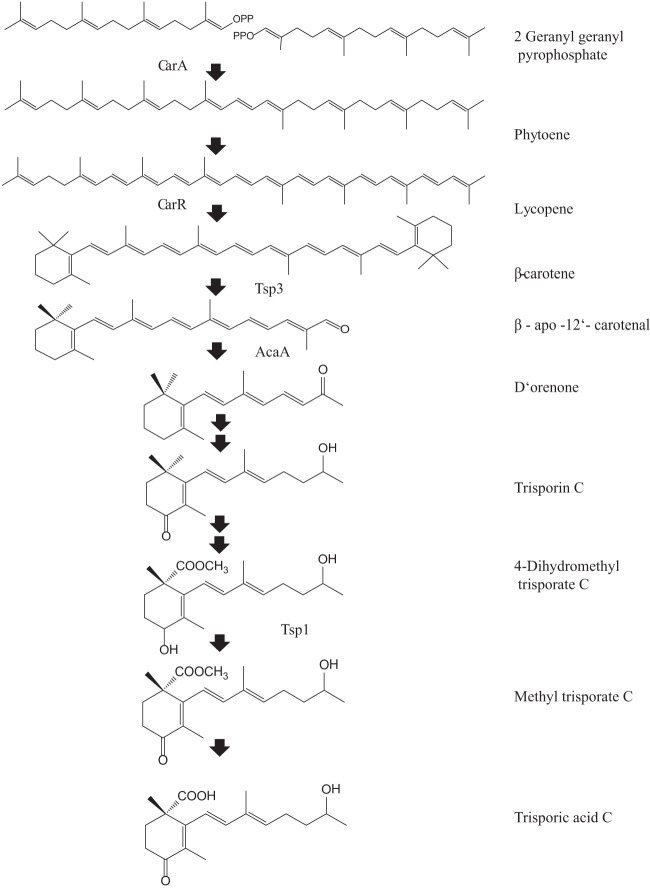
Fig 1.
Schematic diagram of the putative biosynthetic pathway and genes encoding respective proteins involved in β-carotene metabolism. The enzymes depicted left of the arrows lead to β-carotene biosynthesis, while those to the right of the arrows are involved in trisporic acid biogenesis. CarRA is a bifunctional enzyme having 2 domains, CarR and CarA, that lead to biogenesis of β-carotene. The first apocarotenoid formed by carotenoid cleavage oxygenase (TSP3) is further cleaved down to C18 trisporoid compounds. A double black arrow indicates more than one step is involved in formation of the subsequent metabolite.