Fig 2.
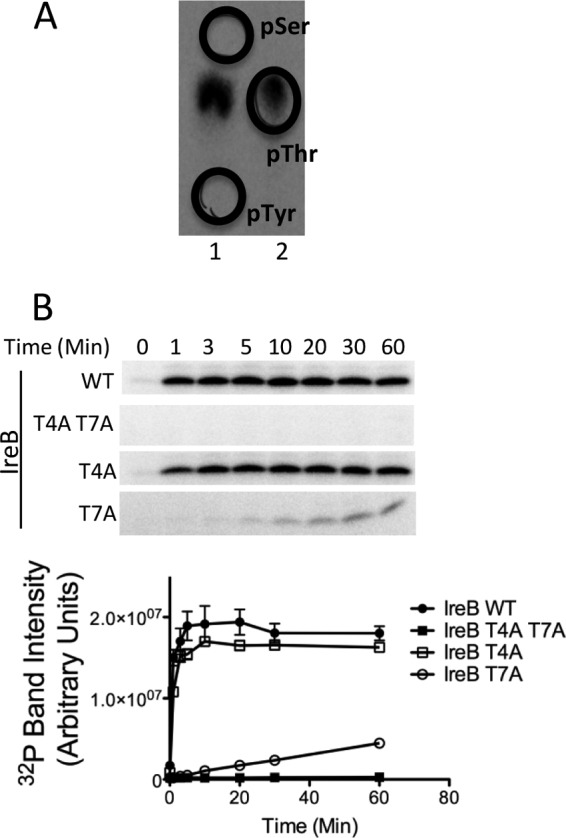
IreK-n phosphorylates IreB on threonine residues. (A) Phosphoamino acid analysis on IreB phosphorylated by IreK-n in vitro. Radiolabeled phospho-IreB protein was subjected to acid hydrolysis and separated by high voltage electrophoresis in 2 adjacent lanes of a cellulose TLC plate. To facilitate unambiguous identification of the phosphorylated amino acid derived from IreB, phosphoamino acid standards were mixed with the IreB hydrolysate and applied in separate lanes (lane 1, phospho-Ser + phospho-Tyr; lane 2, phospho-Thr) and their positions marked (black circles) after staining with ninhydrin. All detectable radiolabeled signal derived from IreB comigrated with the phosphothreonine standard. (B) Kinase assays were performed with 0.33 μM IreK-n and 14.2 μM recombinant hexahistidine-tagged IreB (WT, wild-type IreB; point mutants with substitutions as indicated). Reactions were performed in kinase buffer containing 2 mM ATP, 1 μCi [γ-32P]ATP at 37°C for the indicated times. Radiolabeled proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimaging. Gel images are representative of three independent replicates. Points on the graphs represent the mean and SEM of all three independent replicates.
