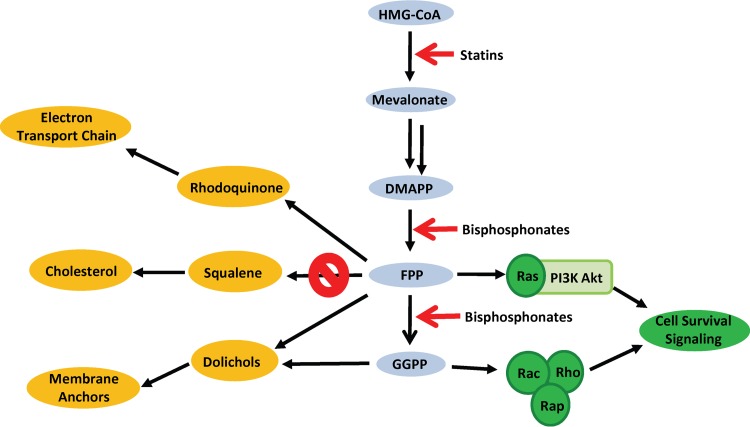
Fig 1.
Schematic representation of the mevalonate pathway in Schistosoma mansoni. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzymeA (HMG-CoA), the product of HMG-CoA synthase, is converted to mevalonate by HMG-CoA reductase, the target of the cholesterol-reducing statins. A series of reactions converts mevalonate to dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP), which is converted to its isomer, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP). Condensations of one DMAPP and one IPP to produce geranyl diphosphate (GPP) and of IPP with GPP to form farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) are carried out by FPP synthase (FPPS) and are the targets of bisphosphonate therapies. Condensation of FPP and IPP leads to the production of geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) by GGPP synthase (GGPPS). FPP is used to synthesize various quinones, GGPP is used to synthesize dolichols, and both are essential in the posttranslational prenylation of a variety of proteins (e.g., the small GTPases Ras, Rab, and Rho) that are important for cell signaling and survival. Rhodoquinone plays a crucial role in the electron transport chain during cellular respiration in S. mansoni mitochondria. Conversion of FPP to squalene does not occur in S. mansoni, and therefore, there is no cholesterol synthesis.