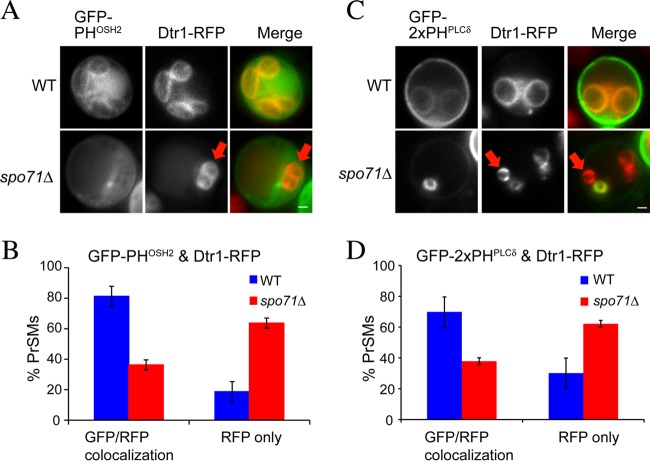
Fig 2.
Effect of the spo71Δ mutation on prospore membrane PtdIns(4)P and PtdIns(4,5)P2 pools. (A) Sporulating wild-type (AN120) and spo71Δ (AN363) cells expressing both a PtdIns(4)P sensor (GFP-PHOSH2) and a prospore membrane marker (Dtr1-RFP). The red arrows indicate a prospore membrane without the GFP marker in the spo71Δ cell. Bar, 1 μm. (B) Quantitation of GFP-PHOSH2/Dtr1-RFP colocalization. Bars indicate standard errors of the means. More than 100 prospore membranes were scored in each of four separate experiments. (C) Sporulating wild-type (AN120) and spo71Δ (AN363) cells expressing both a PtdIns(4,5)P2 sensor (GFP-2xPHPLCδ) and a prospore membrane marker (Dtr1-RFP). The red arrows indicate a prospore membrane without the GFP marker in the spo71Δ cell. Bar, 1 μm. (D) Quantitation of GFP-PHPLCδ/Dtr1-RFP colocalization. Bars indicate standard errors of the means. More than 100 prospore membranes were scored in each of two separate experiments. The chi-square test indicates that the differences between wild-type and spo71Δ cells are significant (P < 0.001).