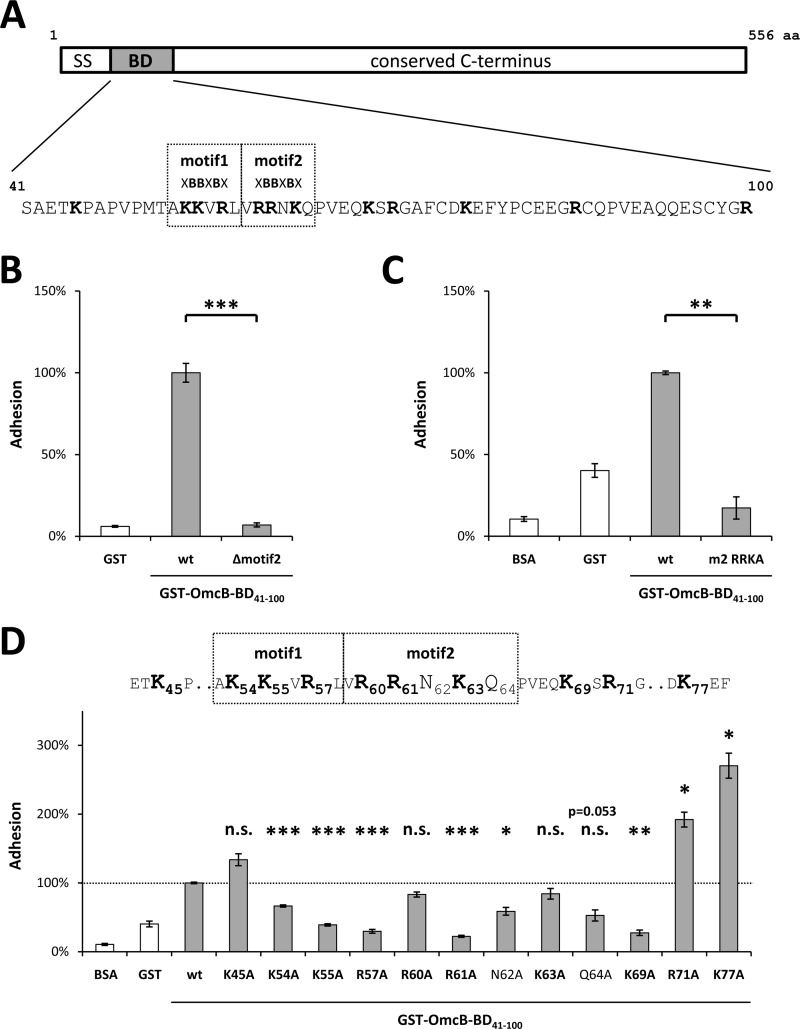
Fig 2.
Single amino acids within the binding domain (BD) differ in their impact on the binding properties of C. pneumoniae OmcB. (A) Schematic depiction of C. pneumoniae OmcB, together with the sequence of the binding domain (amino acids 41 to 100). Heparin-binding motifs (XBBXBX) are boxed, basic amino acids are in boldface. SS, signal sequence. (B) Adhesion of protein-coated latex beads to human HEp-2 cells. A total of 1 × 106 HEp-2 cells were incubated with 1 × 107 beads coated with either recombinant GST (rGST) or rGST-tagged wild-type OmcB-BD (wt) or rGST-tagged OmcB-BD lacking the second heparin-binding motif (Δmotif2). The number of beads bound by 1,000 HEp-2 cells was determined microscopically. Binding of wt OmcB-BD was set to 100% adhesion (n = 4). (C and D) Adhesion of protein-coated, fluorescent latex beads to human HEp-2 cells. A total of 1 × 106 HEp-2 cells were incubated with 1 × 107 fluorescent beads. Adhesion was quantified by measuring the overall fluorescence of attached beads per 1 × 105 HEp-2 cells by flow cytometry. Binding of wt OmcB-BD was set to 100% adhesion. (C) Beads were coated with either rGST, BSA, rGST-tagged wild-type OmcB-BD (wt), or an rGST-tagged variant of OmcB-BD in which all three basic amino acids in the second heparin-binding motif were replaced by alanines (m2 RRKA). (n = 3). (D) Beads were coated with either rGST, BSA, or rGST-tagged wild-type OmcB-BD (wt) or with rGST-tagged OmcB-BD variants in which single amino acids were replaced by an alanine residue as indicated. Heparin-binding motifs (XBBXBX) are boxed, and basic amino acids are in boldface (n = 3). Statistically significant differences are denoted by ***, **, and *, which indicate P < 0.001, P < 0.01, and P < 0.05, respectively. n.s., not significant.