Fig 3.
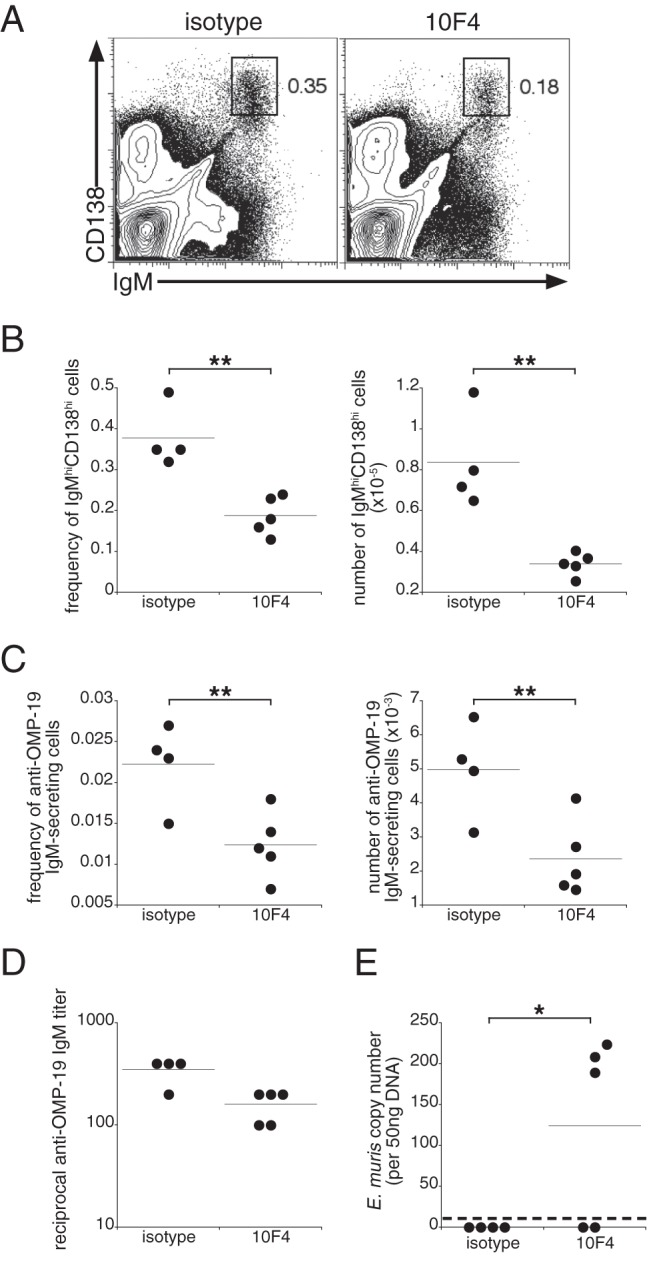
BAFF signaling is required for the maintenance of IgM production during chronic infection. (A) A BAFF-neutralizing antibody was administered on days 63, 70, and 77 postinfection, and bone marrow cells were analyzed for surface expression of IgM and CD138 on day 79 postinfection. The gated regions indicate the long-term IgM-producing plasmablasts identified in our previous studies (1), and percentages are given on the right. (B) Frequency and number of IgMhi CD138hi bone marrow plasmablasts identified using the gating strategy shown in panel A. (C) Frequency and number of OMP-19-specific IgM-secreting cells enumerated by an ELISPOT assay. Data represent values calculated from one femur and tibia for each mouse. (D) Titers of OMP-19-specific IgM in sera from control and treated mice. (E) Peritoneal exudates were isolated from mice on day 79 postinfection, and E. muris copy numbers were determined using quantitative PCR. The dashed line indicates the limit of detection of our assay. The data are representative of two experiments using 4 to 5 mice per group. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.
