Fig 6.
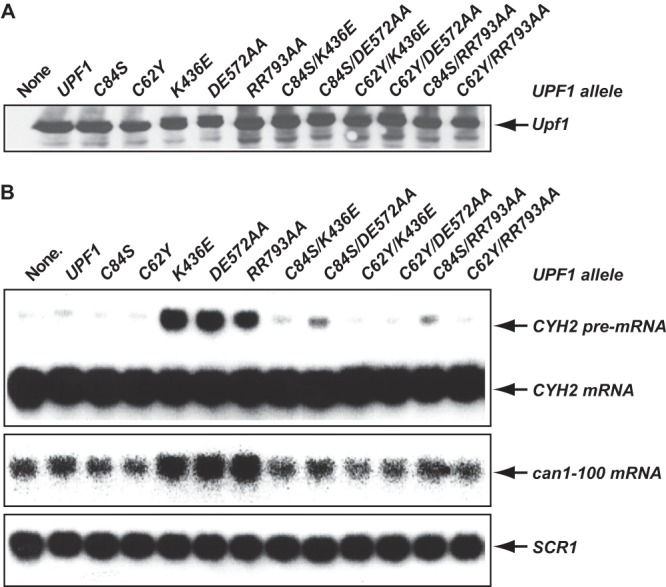
Mutations in the CH domain that weaken Upf1 intramolecular interactions eliminate the dominant-negative effects on NMD resulting from mutations in the RNA helicase domain. Specific amino acid substitutions were introduced into the CH domain or the RNA helicase domain or both domains of Upf1. The resulting upf1 alleles were cloned into pYX142 and individually transformed into the wild-type strain HFY114. Whole-cell extracts and total RNA were prepared from each of the resulting strains. (A) The levels of Upf1 protein in these strains were analyzed by Western blotting, using a polyclonal antibody against Upf1. (B) The steady-state levels of the CYH2 pre-mRNA and the can1-100 mRNA in these strains were analyzed by Northern blotting, using random-primed probes specific for CYH2, CAN1, or SCR1 transcripts as described in the legend to Fig. 5A.
