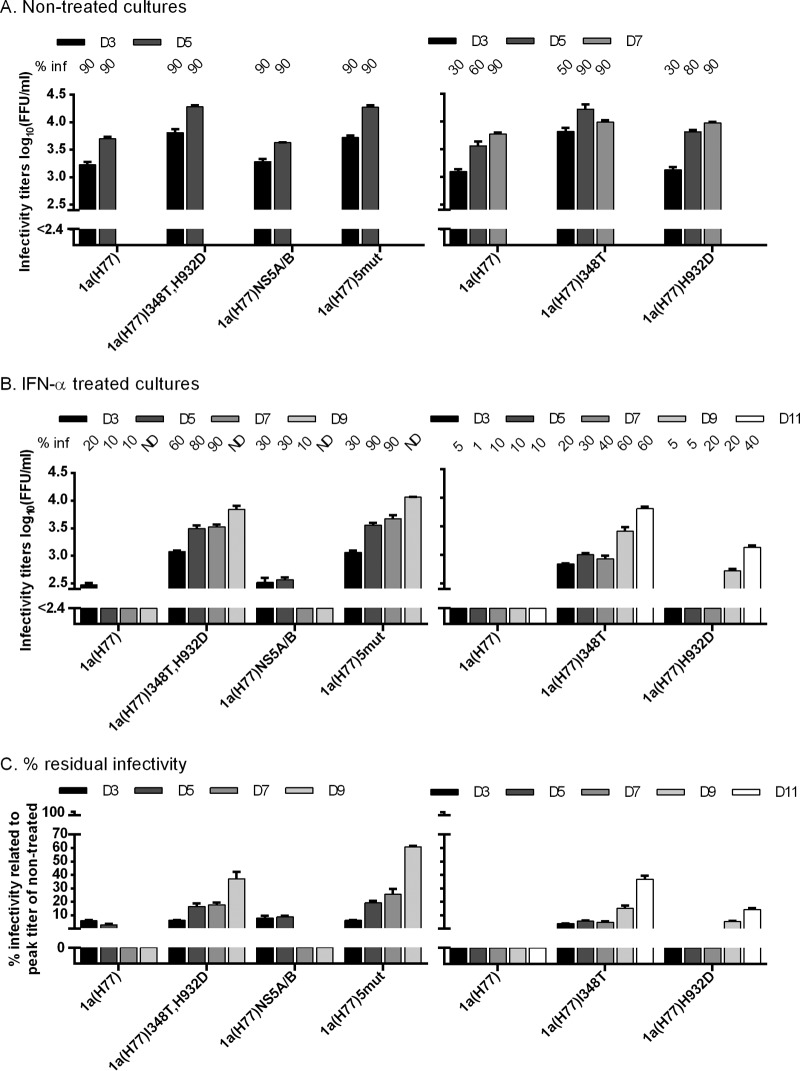
Fig 2.
I348T in E1 increased infectivity titers of 1a(H77) and conferred IFN-α resistance. In vitro HCV RNA transcripts of the indicated recombinants were transfected into replicate Huh7.5 cultures. From day 1 posttransfection, cultures were split every second day. (A and B) The percentage of infected cultured cells (% inf) was monitored by immunostaining for HCV NS5A and is indicated above the graph at the indicated day posttransfection. ND, the percentage was not determined. Supernatant HCV infectivity titers are shown as means from 3 replicates with standard errors of the means (SEM). The lower limit of detection in the experiments shown was up to 2.4 log10 FFU/ml, indicated by the y axis breaks. (A) Cultures were monitored without IFN-α treatment until viruses had spread to almost all cultured cells. (B) Replicate cultures were treated with 20 IU/ml of IFN-α2b on day 1 posttransfection and subsequently each time the cells were split. Cultures were monitored until the fittest virus had spread to almost all cultured cells. 1a(H77)I348T and 1a(H77)H932D only spread to a maximum of 60 and 40% of cells, respectively, followed by a decrease in percent infected cells. (C) Percent residual infectivity was determined by relating infectivity titers of treated cultures to peak infectivity titers of nontreated cultures infected with the same recombinant.