Fig 1.
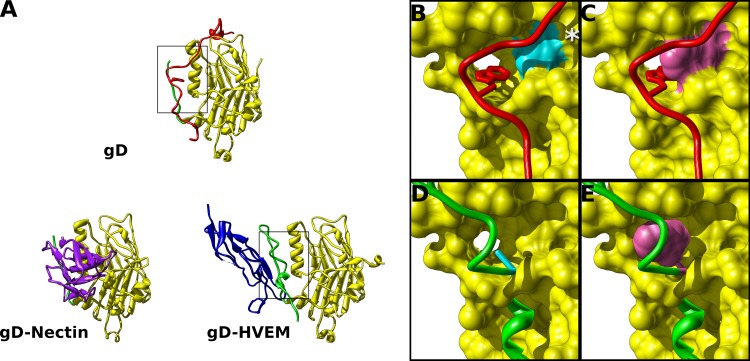
Mutations designed to displace the gD C terminus. (A) Structures of gD alone or gD bound to HVEM or nectin-1 depict the receptor binding interface of gD. The C terminus (red) lies across the interface that binds either HVEM or nectin-1. Boxed regions are enlarged in panels B through E. (B) When receptor is not bound, W294 (stick representation) of the C terminus binds in a hydrophobic pocket formed by helix 3 of the gD core (box in panel A). V231 (cyan) is at the back of this pocket. (C) Mutating V231 to tryptophan (purple) was predicted to prevent W294 from binding in the hydrophobic pocket. (D) From the structure of gD bound to HVEM, the N terminus of gD forms a hairpin (green), and HVEM Y23 binds in the same hydrophobic pocket of gD. Residue A12 (cyan) makes up an edge of this hydrophobic pocket. By overlaying the gD N-terminal hairpin of the HVEM bound structure on the gD core of the unbound structure, A12W is positioned near the same hydrophobic pocket bound by W294. (E) Mutating A12 to tryptophan (purple) was predicted to fill this hydrophobic pocket, inducing the N-terminal hairpin to form even when HVEM is not bound. The asterisk in panel B denotes S140. Mutation S140N introduces an N-linked glycan and has been implicated in receptor-independent virus entry.