Fig 2.
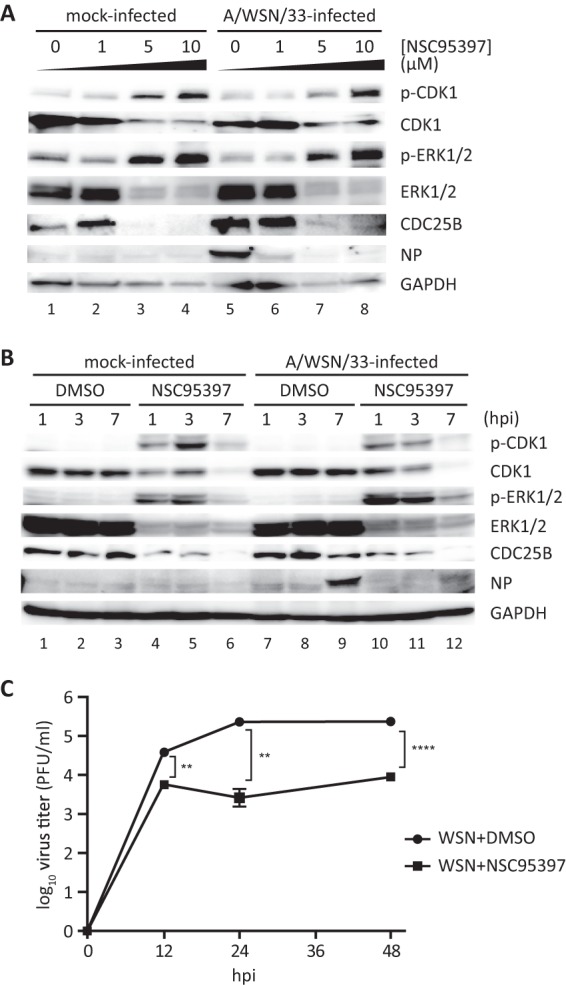
NSC95397 treatment resulted in increased levels of phosphorylated CDK1 and ERK1/2. (A) BEAS2B cells were treated with DMSO (0 μM) or increasing doses of NSC95397 (1, 5, or 10 μM). At 1 h posttreatment, cells were mock infected or infected with influenza A/WSN/33 virus at MOI = 1. Cells were harvested for protein analyses at 7 hpi. (B and C) Cells were treated with DMSO or 5 μM NSC95397. At 1 h posttreatment, cells were mock infected or infected with influenza A/WSN/33 virus at MOI = 1 (B) or MOI = 0.05 (C). (B) Cells were harvested for protein analyses at 1, 3, or 7 hpi. To determine effects of NSC95397 treatment in dephosphorylation of CDC25B targets CDK1 and ERK1, protein lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using phosphospecific and total CDK1 and ERK1/2 antibodies. Levels of cellular CDC25B, GAPDH, and viral NP proteins were also evaluated. (C) At 12, 24, and 48 hpi, culture supernatants were collected and titrated on MDCK cells. **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.
