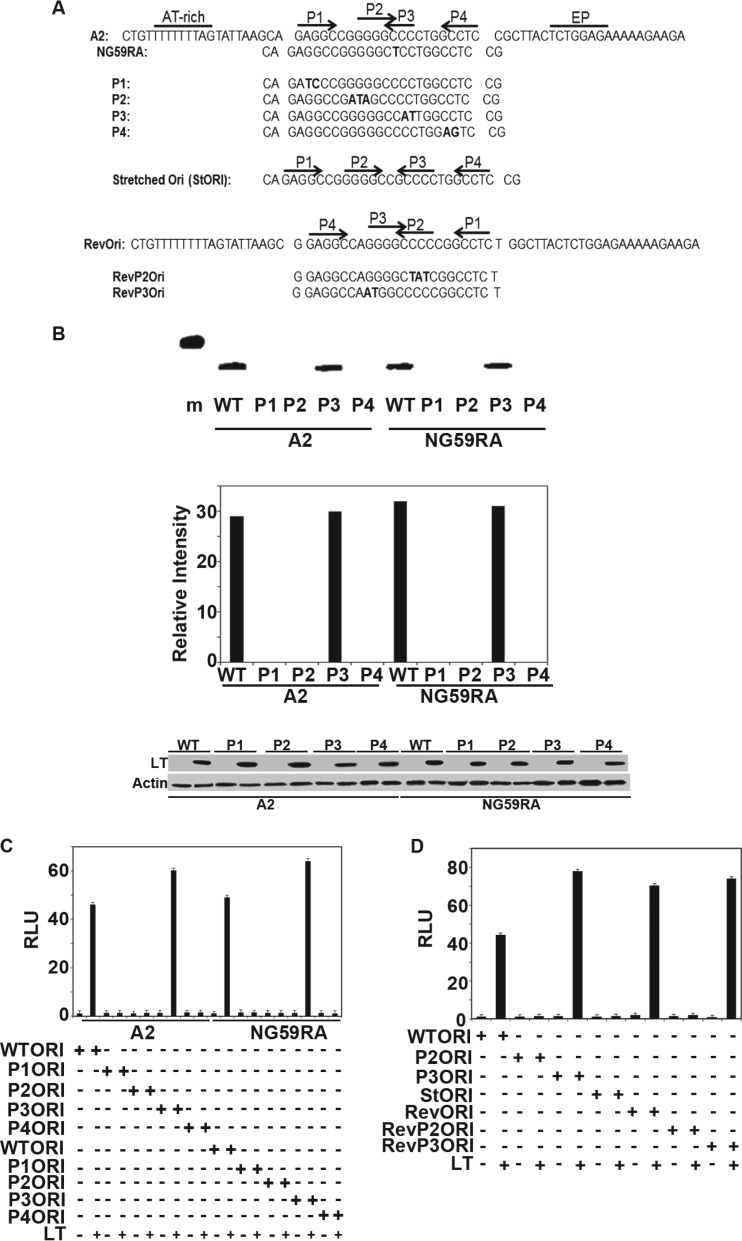
Fig 5.
Replication assays. (A) Origin sequences of wild-type and mutant A2 and NG59RA origin regions. (B) (Top) NIH 3T3 cells were transiently transfected with wild-type A2 or the NG59RA polyomavirus origin-containing plasmid pFLORI40 or their respective mutants P1, P2, P3, or P4, together with LT, for 48 h. Low-molecular-weight DNA prepared according to the Hirt protocol was digested with DpnI. Replicated DNA was amplified using PCR analysis with specific primers and visualized by ethidium bromide (EtBr) staining of the 1.5% agarose gel. (Middle) The signals from replicated DNAs from 10-thermal-cycle PCRs (Top) were quantified using Image J software. (Bottom) Lysates from the replication assay (Top) were analyzed by Western blotting for expression of LT. Lysates from cells transfected with control vectors that have no LT were used as the negative control. Actin was used as a loading control. A 500-bp marker is shown in lane m. (C) Extracts from NIH 3T3 cells transiently transfected with wild-type A2, NG59RA, or their mutant (P1, P2, P3, and P4) origin luciferase reporter vectors and large T or control vectors, along with CMV beta-galactosidase, were tested for luciferase and beta-galactosidase activities approximately 40 h after transfection. The values were set to 1 for the wild-type origin and wild-type LT. The error bars represent the standard errors of the mean. (D) Extracts from NIH 3T3 cells transfected with wild-type A2 origin luciferase reporter vector or its mutants (P2 and P3) or inverse complement origin (Revori) or its mutants (RevP2 and RevP3) and large T or control vectors, along with CMV beta-galactosidase, were tested for luciferase and beta galactosidase activities approximately 40 h after transfection. The values were set to 1 for the wild-type origin and wild-type LT. The error bars represent the standard errors of the mean.