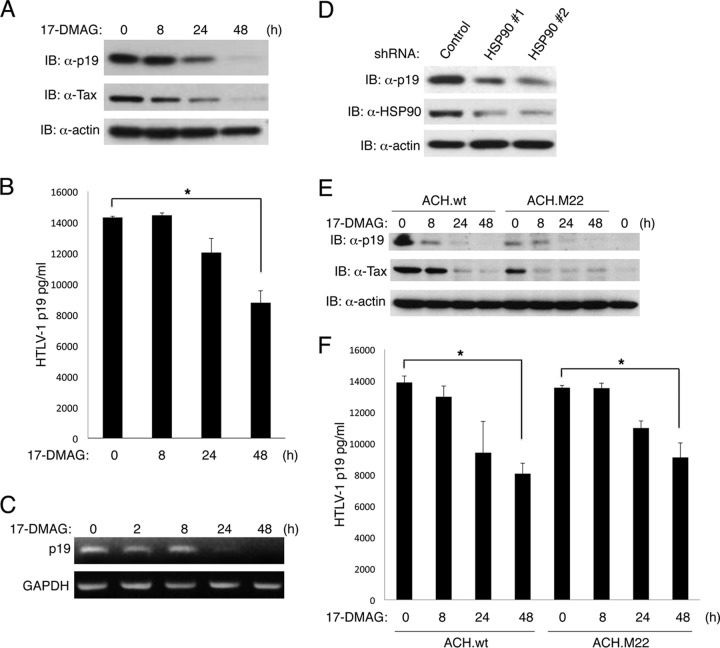
Fig 5.
Inhibition of HSP90 blocks HTLV-1 replication. (A) MT-2 cells were treated with 17-DMAG (0.5 μM) for the indicated times, and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-HTLV-1 p19, anti-Tax, and antiactin. (B) Supernatants from MT-2 cells shown in panel A were subjected to HTLV-1 p19 ELISA. (C) MT-2 cells were treated with 17-DMAG (0.5 μM) for the indicated times, and RNA was extracted for RT-PCR with p19 and GAPDH primers. (D) MT-2 cells were infected with lentiviruses expressing control or HSP90 shRNAs. Immunoblotting was performed with anti-HTLV-1 p19, anti-HSP90, and antiactin. (E) 293T cells were transfected with HTLV-1 proviral clones ACH.wt or ACH.M22, and after 24 h cells were treated with 17-DMAG (0.5 μM) for the indicated times. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-HTLV-1 p19, anti-Tax, and antiactin. (F) Supernatants of 293T cells from panel E were subjected to HTLV-1 p19 ELISA. Error bars represent the standard deviations of triplicate samples (*, P < 0.05).