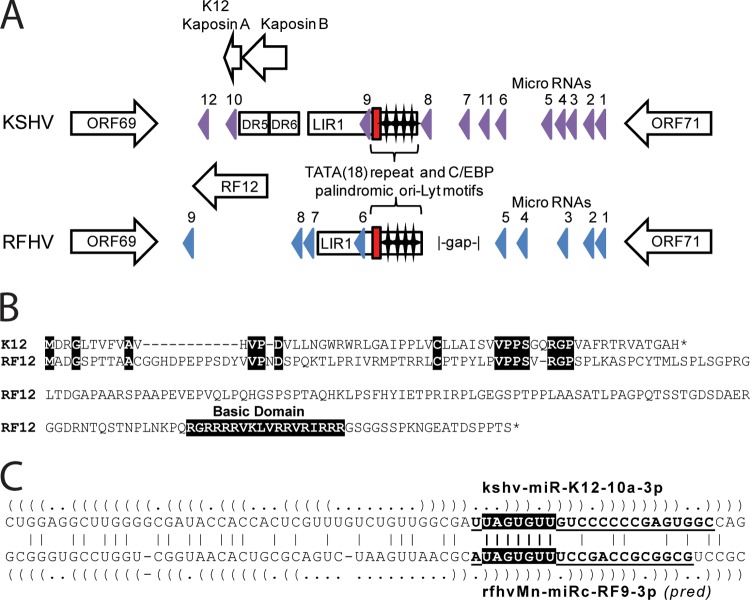
Fig 7.
Comparison of the divergent D loci of RFHVMn and KSHV. (A) Graphical representation of the structure of the Ori-Lyt-R regions of KSHV (NC_009333) and RFHVMn (KF703446) between ORF69 and ORF71; the presence of encoded proteins and microRNAs is shown. The position of the 18-bp TATA repeat (red box) and C/EBP palindromic motifs (stars) are indicated. The known KSHV microRNA genes (purple) and the predicted RFHVMn candidate microRNAs with bona fide pre-microRNA hairpins (blue) are shown. (B) Alignment of ORF K12 (YP_001129428) and the positional ORF RF12 (AGY30757) homolog. Identical residues and the basic domain of RF12 are highlighted. (C) Alignment of the kshv-miR-K12-10a-3p and rfhvmn-miRc-RF9-3p pre-miRNAs. The predicted hairpin structures are indicated by parentheses. Boldface and underlined letters denote sequences of the mature kshv-miR-K12-10a-3p RNA (74) and the mature rfhvmn-miRc-RF9-3p, as predicted (pred) according to the guidelines of Zeng et al. (75). The conserved seed sequences are highlighted.