Figure 1.
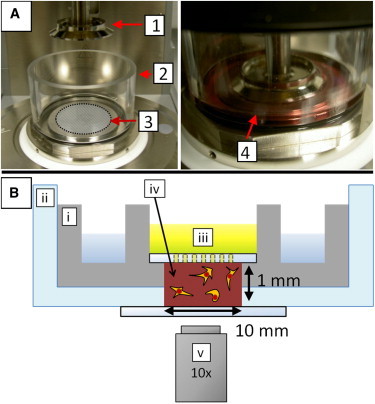
Experimental assays. (A) The viscoelastic properties of cell-populated fibrin gels were measured with a stress-controlled rheometer (left). The top plate is a cone (1) of 40 mm in diameter and 1° angle. The fibrin solution was pipetted on the bottom plate (3), the top plate was quickly lowered (right), and the fibrin was allowed to polymerize in situ at 37°C. The gel was immersed in cell culture medium supplemented with serum (4), using a Perspex ring (2). (B) Schematic representation of the custom-designed microscope holder used for observing cells spreading in fibrin gels (not drawn to scale). The sample (iv) was confined in a stainless steel well (i) topped with a glass plate with holes to enable medium (iii) exchange. The entire geometry was contained in a glass bottom dish (ii). Cell spreading was observed by bright field microscopy using a 10× air microscope objective (v). To see this figure in color, go online.
