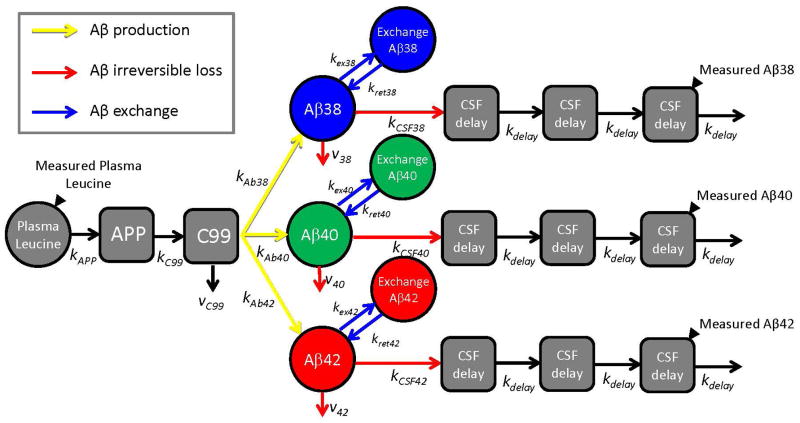
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of compartmental model of Aβ38, Aβ40, and Aβ42 metabolism.
Solid black triangles depict sampling sites for plasma leucine and CSF Aβ peptides. Production of Aβ peptides is signified by yellow arrows, exchange by blue arrows, and irreversible loss by red arrows. The model incorporated the labeling time course of plasma 13C6-leucine, APP production and processing to C99 peptide, and Aβ38, Aβ40, or Aβ42 production from C99. The labeled Aβ38, Aβ40, and Aβ42 that are sampled in CSF are presumed to be soluble within the “brain” compartment. The soluble Aβ peptides may exchange with other unlabeled Aβ structures, may be transported to CSF, or may be lost due to other processes (e.g. transport to blood, plaque deposition, or cellular degradation). Transport through CSF is modeled as a three compartment time delay.