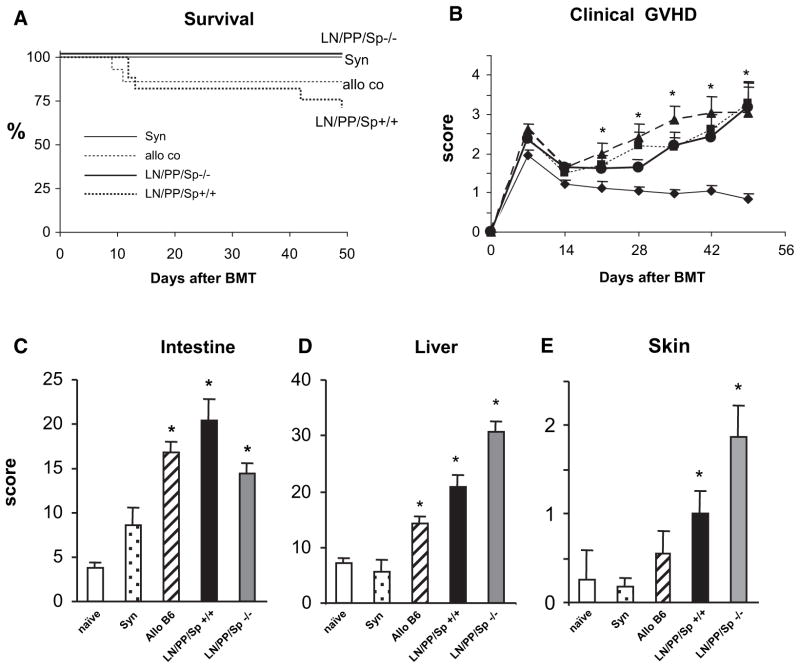
Figure 2.
Splenectomized, aly/aly (LN/PP/Sp−/−) mice develop significant clinical and target organ GVHD following allo-BMT from MHC-mismatched Balb/c donors. Lethally irradiated, splenectomized aly/aly mice (LN/PP/Sp−/−) received BMT from syngeneic aly/aly or allogeneic Balb/c donors as described in the Materials and Methods section. Littermate, sham splenectomized aly/+mice (LN/PP/Sp+/+) served as allo-BMT controls. In some experiments, wild-type C57BL/6 recipients of C57BL/6 or Balb/c BMT served as additional negative and positive GVHD controls, respectively. The severity of GVHD was subsequently assessed by survival (A) and clinical score (B).◆ syngeneic, ■ C57BL/6, ▲ LN/PP/Sp+/+, ● LN/PP/Sp−/−. Target organ histopathology in the intestinal tract (C), liver (D), and skin (E) was also examined in surviving mice 6 to 7 weeks after BMT. Histology scores from naïve, untransplanted aly/aly mice are also shown. Data are expressed as mean±SEM from of 4 (survival and clinical score) or 3 (target organ pathology) different experiments. n = 12 to 18, (survival and clinical score) or 6 to 12 (pathology) per group; *P<.01 compared to syn controls. naïve aly/aly □; syn
 ; allo-C57BL/6 cont ▨; LN/PP/Sp+ ■; LN/PP/Sp−/−
; allo-C57BL/6 cont ▨; LN/PP/Sp+ ■; LN/PP/Sp−/−
 .
.