Figure 3.
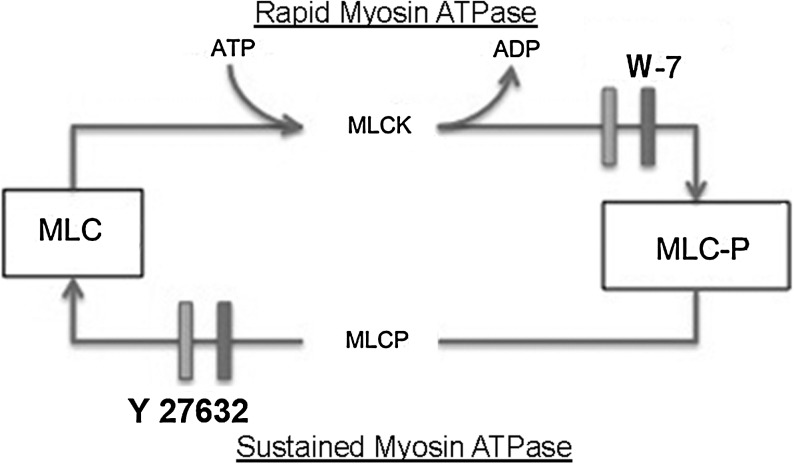
A diagram of the scheme for the rapid and sustained myosin ATPase is presented. The phosphorylation of MLC in rapid and sustained myosin ATPase activity occurs by different mechanisms. MLCK affixes a phosphate group from ATP onto MLC serine-19, which is necessary for optimal myosin ATPase activity. The inhibitor W-7 will block MLCK, thus inhibiting rapid myosin ATPase activity. MLCP removal of the phosphate group from MLC serine-19 is required for the relaxation step in cell locomotion through rapid myosin ATPase activity. Inhibiting MLCP activity, prolonging the phosphorylated state of MLC, defines the mechanism for sustained myosin ATPase activity, where MLCP is maintained in a chronic state. The inhibitor Y-27632 restores MLCP activity and terminates sustained myosin ATPase activity. MLC, myosin light chain; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase; MLCP, myosin light chain phosphatase.