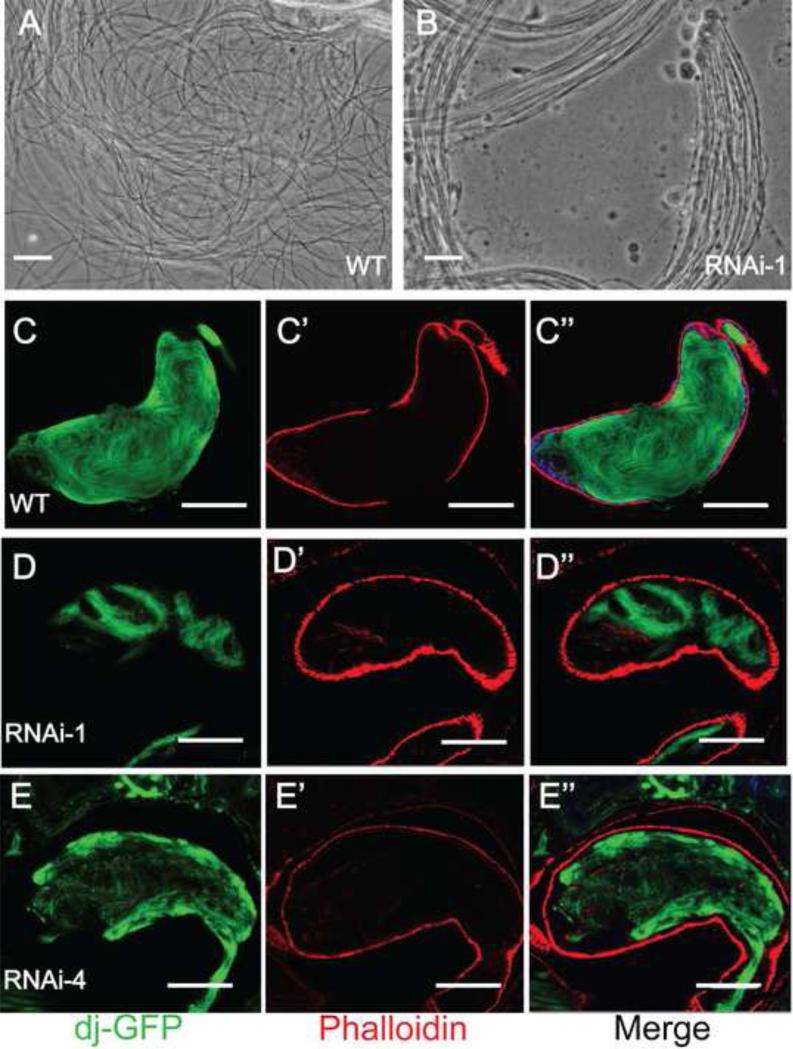
Fig. 3.
Gudu knockdown caused sperm maturation defects. Panels A and B are phase contrast images of elongated individual sperms from testes of a 2 day-old WT male (A) and bundled spermatids from a 2 day-old Gudu RNAi male (B). Note the smooth texture of individual sperm released from the squashed WT testis. In contrast, there was frequent bundling of sperms in testes of the RNAi males. Panels C to E” are DAPI and rhodamineconjugated phalloidin stained seminal vesicles of WT and Gudu RNAi lines, where the GFP tagged Don Juan protein was expressed to illustrate sperm tails. In C, abundant loose individual sperms were seen in seminal vesicle from WT male fly. In D and E, the seminal vesicles from RNAi-1 and RNAi-4 lines contained very few sperms. Scale bars in A and B, 10 µm; C-C”, 100 µm; D-E”, 50 μm. Green is dj-GFP, red is phalloidin, and blue is DAPI.