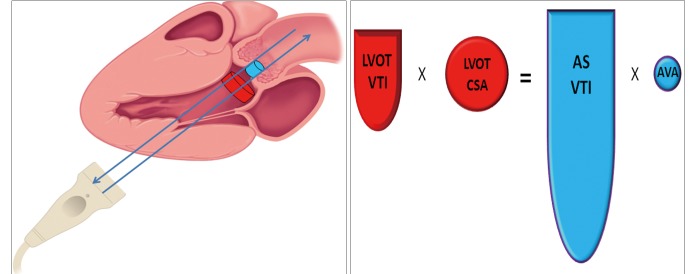
Figure 3.
Continuity Equation. The continuity equation is derived from the basic principles of conservation of mass. The stroke volume below the valve must be the same as the stroke volume through the valve. The flow in LVOT can be calculated from the product of the cross sectional area of the LVOT (red circle) and the velocity time integral (VTI) of the pulsed Doppler of LVOT (area of the red waveform). That flow must be constant through the valve, so the effective orifice area of the stenotic valve can be easily calculated by dividing this stroke volume by the VTI of the continuous Doppler of AVA (area of the blue waveform)