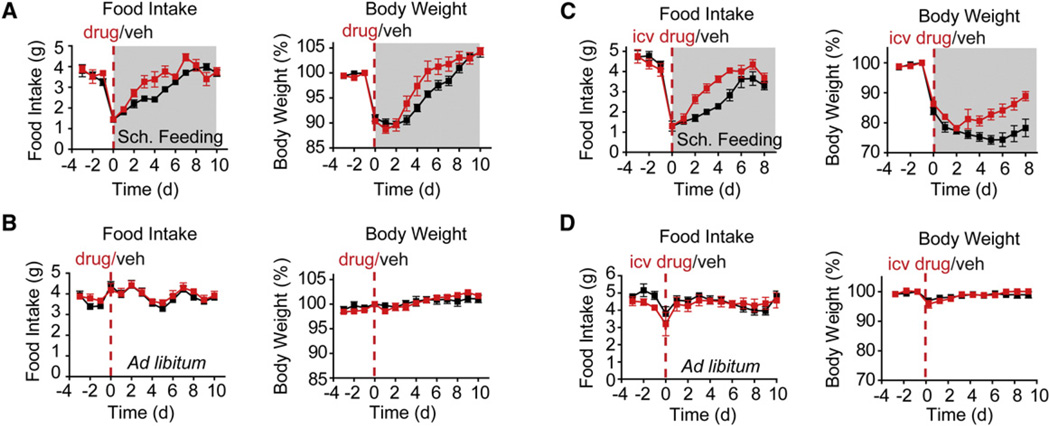
Figure 7. KOR Signaling Restrains Food Intake during Scheduled Feeding.
Mice were treated with KOR inhibitors (red) or vehicle (black) by central or peripheral injection, and their food intake and body weight were recorded during ad libitum or scheduled feeding (gray).
(A) Mice givenanintraperitoneal injection ofthe KOR antagonistJDTic (red) orvehicle (black) and switched from adlibitum toscheduled feedingon day 0.p=0.01 for the difference in cumulative food intake on days 2–7. p = 0.055 for the body weight difference for days 4–7.
(B) Mice given an intraperitoneal injection of JDTic (red) or vehicle (black) and maintained on an ad libitum diet.
(C) Mice given an icv injection ofthe KOR antagonist norbinaltorphimine (red)orvehicle (black). Mice were switched from adlibitum toscheduled feedingonday 0. p < 0.01 for the difference in food intake for days 2–5 by t test. p < 0.02 for difference in body weight for days 5–8.
(D) Mice given an icv injection of the norbinaltorphimine (red) or vehicle (black) and fed ad libitum.
All error bars are mean ±SEM; p values calculated by two-tailed unpaired t test.