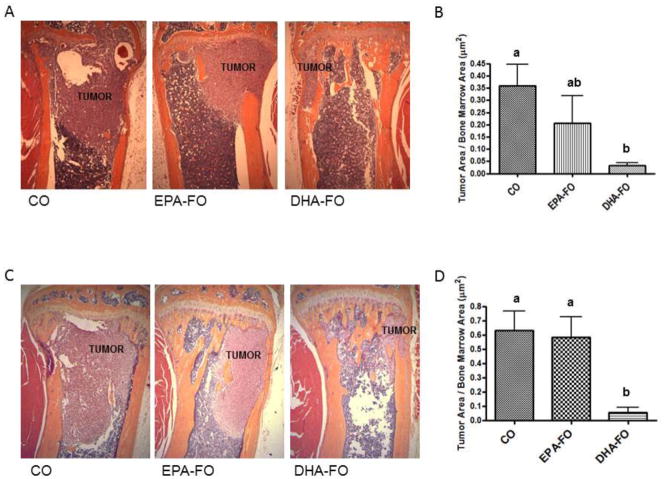
Fig. 2. Effect of EPA and DHA on breast cancer metastasis to bone after intra-cardiac injection of breast cancer cells.
The athymic NCr-nu/nu female mice were fed a diet containing CO or EPA-FO or DHA-FO for 4 weeks prior to the intra-cardiac injection of the MDA-MB-231 (A) or MDA-MB-231-Luc (C) cells. The mice were then injected with 1 × 105 cells in 100 μl of PBS intra-cardially. The mice were maintained in their respective diets for 4 weeks post injection. After x-ray, mice were sacrificed and bones were collected and fixed in formalin. After decalcification, paraffin embedded bone sections were prepared and stained for H&E to determine the breast tumor burden in bones. Histomorphometry of tumor burden area was done for MDA-MB-231 (B) or MDA-MB-231-Luc (D). n=5 mice per group. Each value represents the mean ± SEM. Value with different superscripts are significantly different at P<0.05 by Newman Keuls one way ANOVA with multiple comparison test.