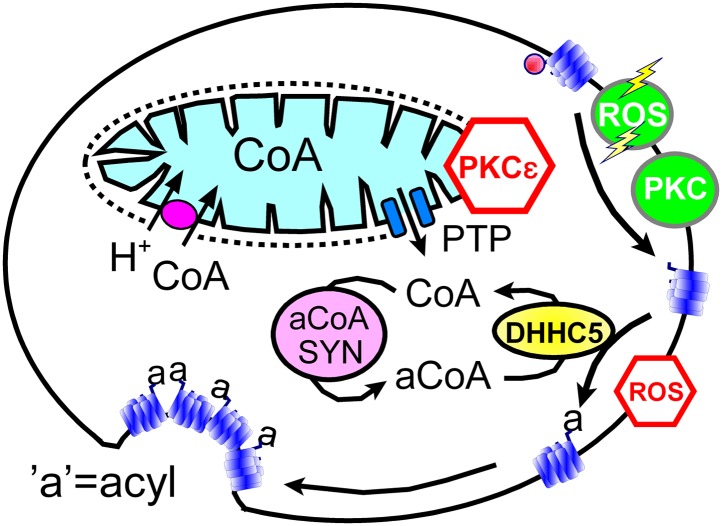
Figure 8. Hypothetical MEND pathway.
Mitochondria accumulate CoA via voltage-dependent transporters that are probably proton-coupled (Tahiliani, 1989). CoA can be released in response to PTP openings, either directly or more slowly via reverse CoA transport during mitochondrial depolarization. During a MEND response the activation of PKCs will restabilize mitochondria and promote MEND progression at the cell surface. PTP openings are inhibited when PKCs are activated ‘prior’ to the MEND protocol. Acyl CoA transients occur upon release of CoA because acyl CoA synthetases are CoA-limited (Idell-Wenger et al., 1978). We speculate that conventional PKCs and ‘transient’ oxidative stress increase the availability of palmitoylation sites at the surface membrane, whereas the immediate presence of ROS inhibits palmitoylation reactions.